Over the past few years, a growing number of businesses have embraced internet tools and services, particularly Software as a Service (SaaS). They are increasingly opting to rent rather than buy software, leveraging online platforms for tasks like invoicing, customer management, lead generation, CRM, and even server hosting.
What Exactly is SaaS?
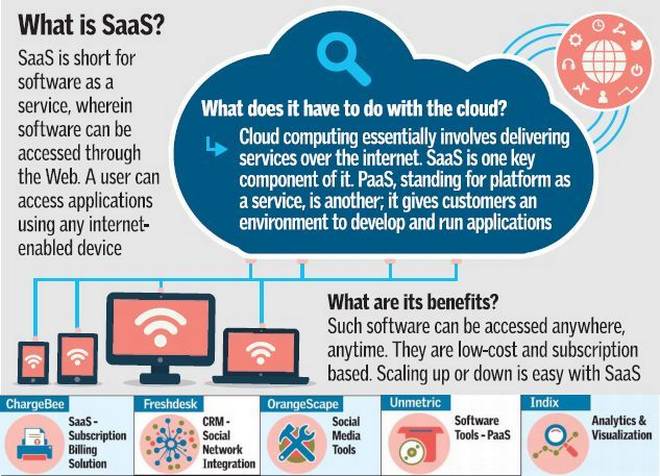
SaaS, short for Software as a Service, signifies a shift from traditional software. Instead of local installation, software is accessed online, available on any device with internet. This model is essentially costs much less..
Think of SaaS as outsourcing your software needs. For instance, instead of investing time and resources in building a landing page, you can subscribe to a SaaS service specializing in it. These platforms simplify landing page creation for a nominal monthly fee. Other SaaS examples include Google’s advertising tools, CRM systems, cloud storage, heatmaps and analytics platforms, and live chat software, among others.
Leading SaaS companies include Salesforce, Linkedin, Workday, Dropbox, Asset Bank, Service Now, New Relic, Zendesk, and many more. A list of the top 250 SaaS companies provides a broader perspective.
Many thriving startups today operate on the SaaS business model measuring model, which allows for predictable revenue and customer churn rates.

Key SaaS Startup Concepts:
MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue): This signifies the predictable revenue generated each month from subscriptions. Growing MRR indicates a healthy business trajectory.
ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue): Similar to MRR but calculated annually, ARR represents the yearly recurring revenue.
ARPU (Average Revenue Per User): ARPU calculates the average revenue generated from each active customer. A low ARPU often indicates a focus on smaller clients rather than enterprises. Increasing ARPU without significant customer loss is a primary goal.
USER CHURN (User Churn Rate): This metric tracks the percentage of users who discontinue their subscriptions within a given period. A lower churn rate is desirable.
Revenue Churn Rate: Unlike user churn, this focuses on revenue lost due to cancellations or downgrades.
LTV (Lifetime Value): LTV represents the total revenue a customer generates throughout their engagement with the business. It’s calculated by ARPU divided by the User Churn rate. LTV helps determine customer acquisition budgets.
CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost): CAC encompasses all costs associated with acquiring a new customer, including sales, marketing, and advertising expenses.
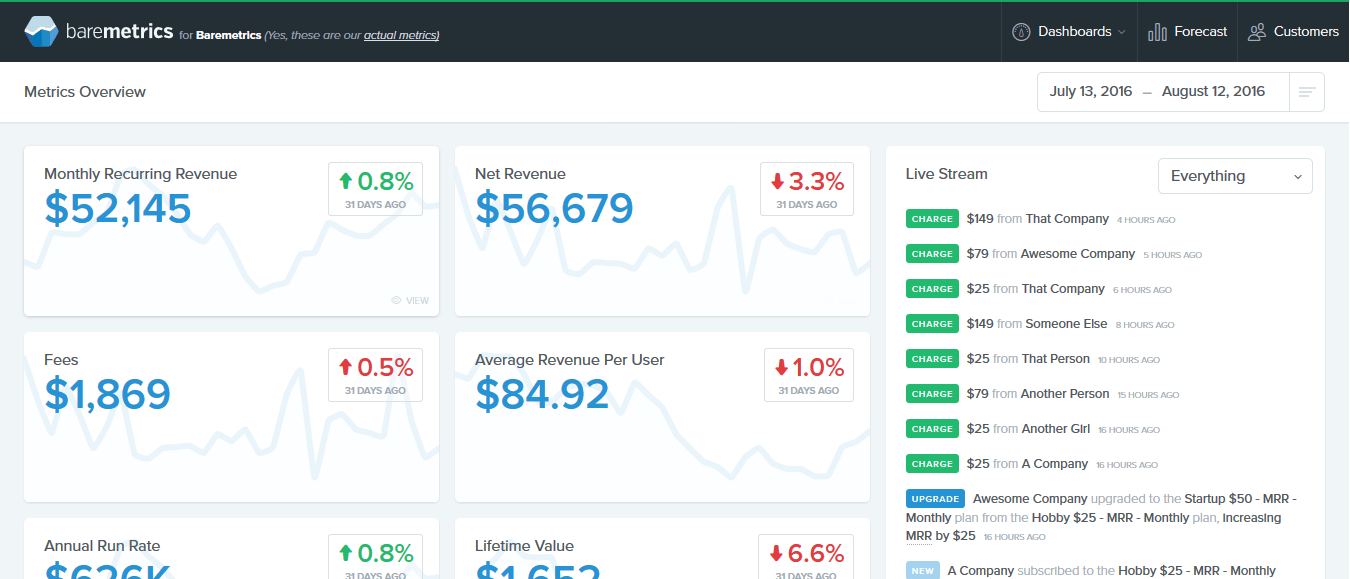
Want to Visualize this Data?
Baremetrics, a SaaS company itself, provides an insightful analytics system for other SaaS businesses using specific payment gateways. It presents the metrics mentioned above in an intuitive and visually appealing manner. Explore their website or those of other SaaS companies for real-world examples.