For those who are fairly new to the world of search marketing, you might have encountered the term “SEO content” being used frequently in marketing discussions. This guide for beginners aims to address three main questions:
- What is SEO content?
- What types of SEO content are there?
- How to develop an SEO content strategy If you have any queries about strategies for SEO content creation that I haven’t addressed here, please feel free to ask in the comments section, and I’ll do my best to answer them here or in a future blog post. Let’s begin!
What is SEO content?
To grasp what marketers mean by SEO content, it’s beneficial to deconstruct the phrase into its individual components:
- “SEO” stands for search engine optimization, which is the process of enhancing a website to make it easily discoverable by users through search engines like Google.
- “Content” encompasses any information available and accessible on the internet (more on the various types of content below). Combining these two ideas, we can define SEO content as any content created with the primary objective of driving traffic to a website from search engines. While this guide won’t cover everything about optimizing content for search engines (that’s a whole other topic), here’s a brief overview of what’s involved in optimizing your web content for SEO:
- Keyword research: Before you start writing, if your goal is to attract traffic organically, it’s crucial to conduct keyword research. This allows you to target keywords with existing search volume—essentially, writing about subjects (or finding keyword niches!) that people are already searching for information on.
- Keyword optimization: Understanding where and how to incorporate keywords strategically within your content is essential for maximum visibility. (For a deeper dive, check out our comprehensive guide to on-page SEO).
- Content organization: Organizing the content on your site logically is not only good for SEO but also enhances user experience, making it easy for visitors to find related content. (The longer they stay on your site, the better.)
- Content promotion: To boost the discoverability of your new content, share it across social media platforms and focus on building links to your content, both internally within your website and externally from other reputable websites.
A quick note on intentions
It’s crucial to remember that if your sole focus is on search engine traffic, your overall results might suffer. To cater to both search engines (which reward you with higher rankings over time) and potential customers and recurring visitors, your content must offer value beyond just SEO. In essence, avoid creating superficial content that might rank well and attract clicks but fails to provide any substantial value to the user. Websites that prioritize such superficial, low-value content risk facing penalties from Google. Additionally, these sites tend to experience high bounce rates and low conversion rates.
Types of SEO content
SEO content can encompass the following:
- Product pages – These are fundamental for any online retail store. A well-crafted product page can effectively function as both SEO content and a dedicated landing page for pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns.
- Blog posts – Maintaining a blog is among the most straightforward methods to generate a consistent flow of valuable SEO content. Generally, blog posts tend to be more engaging and have a higher likelihood of attracting backlinks compared to product pages. Therefore, they can be instrumental in establishing authority for your site. Remember that blogs offer significant flexibility, enabling you to host various content formats mentioned in this list.
 Check out our collection of free SEO-optimized blog post templates.
Check out our collection of free SEO-optimized blog post templates.
- Articles – This category includes news articles, interviews, or feature pieces. Articles are the primary content format found on websites structured like newspapers or magazines.
- Lists – Essentially a type of article, presenting content as a list (e.g., “10 Ways to Reduce Your Electricity Bill” or “101 Things I Dislike About Google”) enhances readability and scannability. Such titles also appear to be more clickable in search engine results pages (SERPs) or social media feeds. And social signals do influence SEO.
- Guides – Guides are comprehensive pieces of content that provide detailed instructions or explanations on a particular topic. While guides can be divided into multiple web pages, it’s recommended to allow users to view long-form content on a single page if they prefer. You can publish a complete guide on your website or offer a summarized excerpt, requiring visitors to submit a registration form to access the full version. While this can be effective for lead generation, remember that placing a registration barrier might reduce the potential organic traffic driven to the guide.
- Videos – Generally, the web has fewer videos than text-based pages. Consequently, achieving a first-page ranking for a competitive keyword might be easier by creating a video instead of an article. Depending on your website or business type, videos can be a highly effective medium for attracting and engaging an audience. Consider creating video tutorials demonstrating how to use your products. Alternatively, visually explain a process relevant to your business – for example, a plumber could create a video showing how to unclog a sink. (SEO tip: Consider adding a text transcript of your video. Explore these additional tips for optimizing videos.)
- Infographics – Infographics are large-format visuals presenting extensive data (often using graphs or charts) on a specific subject. They have the potential to attract significant page views and backlinks. However, since a substantial portion of the content is embedded within the image and not easily interpretable as text by search engines, optimizing other elements of the page becomes crucial. To get started, consider using one of these five free infographic templates.
- Slideshows – Slideshows are a method to showcase a series of related images. In some cases, visuals take precedence over text – for instance, if you aim to present red carpet looks from a recent awards ceremony. Here, optimizing your title, captions, image file names, and other relevant elements becomes vital due to the limited text-based content for search engines to crawl and understand.
- Glossaries – It seems more people utilize Google for definitions than traditional dictionaries. (Do you even recall where your dictionary is?) If your field is specialized, a well-structured glossary can be an effective way to capture organic search traffic. Think culinary terms, medical terminology, fashion jargon, architectural terms, and more.
- Directories – A directory is a curated and organized collection of links pointing to websites or resources related to a specific topic. For example, a perfume blog might create a directory featuring various online and offline perfume retailers, ranging from department stores to independent boutiques across the country. While this list covers some fundamental types of SEO content, it’s not exhaustive. The possibilities for content creation are practically limitless.
How to Develop an SEO Content Strategy
If your content creation process has been somewhat haphazard, hoping for some pieces to eventually rank well, it’s time to adopt a more systematic approach by implementing a well-defined SEO content strategy for the web. Here are four essential steps to define and refine your SEO content strategy:
Define your goals
Start by clearly defining your objectives as a website or business. Are you aiming to generate leads or drive sales through your website? Is your website monetized through ads, and your objective is to increase traffic and cultivate a loyal readership? The answers to these questions will shape the types of content you should prioritize.
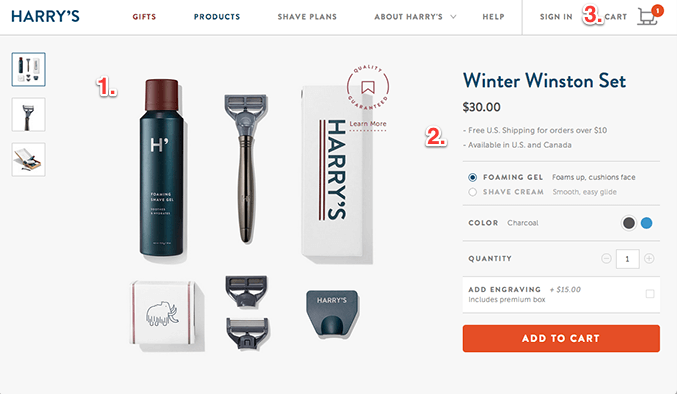
Here’s an excellent example of a minimalist yet sleek and elegant product page If your primary focus is driving product sales, prioritize creating visually appealing and informative product pages optimized for both search engines and conversions. Your secondary focus could be on valuable blog content demonstrating the use cases and benefits of your products, incorporating relevant internal links to product pages where appropriate. (However, it’s best to avoid making your blog solely self-promotional.) If your website operates on an advertising model, prioritizing the acquisition of new readers through organic search is key. Focus on producing high-quality, engaging content, such as long-form articles or comprehensive video resources that are either informative, entertaining, or both. The goal is to create “sticky” content that encourages visitors to stay on your website longer or revisit it.
Consider your audience
Understanding your audience is crucial. Utilize surveys and leverage your analytics software to gain insights into the demographics and behavior of your typical visitor or customer. Consider crafting detailed marketing personas—fictional representations of your ideal website visitors and customers. Then, brainstorm content ideas that would resonate with these personas.
For instance, if you run a B2B website targeting high-level executives, consider creating valuable, in-depth white papers available for download and offline reading. If your target audience consists of teenagers and young adults, prioritize frequent updates with concise text, incorporating more visuals like images and videos. Additionally, ensure your website is fully optimized for mobile devices.
Create an editorial calendar
Once you have a clear understanding of your target audience and your objectives, you can start outlining your editorial calendar. An editorial calendar is essentially a schedule dictating the publication dates of your future content and the specific formats. This helps you maintain a consistent publishing schedule (crucial for blogs), eliminating last-minute scrambles for new content ideas. Here are some valuable tips for creating and adhering to an editorial calendar:
- Use Outlook (or Google Calendar) – Ensure your editorial calendar is accessible to your entire marketing team. Set up reminders for content creators to receive notifications as deadlines approach.
- Consider creating recurring content series – For example, a food blog might feature a meatless recipe every Monday. Numerous blogs publish weekly link roundups (including this one). Create dedicated category pages for each recurring content series, enabling visitors to easily find all your “Meatless Monday” recipes or link roundups in one location.
- Allocate sufficient lead time for creating more complex content formats such as videos and infographics. These often necessitate multiple rounds of edits and can be more demanding in terms of SEO optimization.
- Don’t plan too far ahead – It’s common for editorial calendars to deviate after a month or two due to unexpected shifts in marketing objectives, budget constraints, or staffing changes. Avoid investing excessive time and effort in planning an entire year’s schedule, as it could lead to wasted resources.
Analyze and re-assess
Finally, it’s essential to actively monitor your website’s analytics. Regularly evaluate the performance of your SEO content through comprehensive content audits and technical SEO audits (or even a full-fledged website audit) to identify what’s working effectively and areas that need improvement. Numerous tools and website graders can assist you in this process. Key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success and engagement levels of your content include page views, backlinks, comments (on blog posts and other relevant content formats), social shares (Facebook likes, tweets, etc.), and conversion rates. Your analysis should focus on two primary goals:
- Replicating successful strategies – Identify patterns in your data. Is your audience particularly drawn to video content? If so, create more video content! Adapt your editorial calendar to allocate more time and resources to content formats that resonate strongly with your audience.
- Updating and improving older SEO content – If you optimized an article for a specific keyword but notice it’s attracting traffic for a different variation of that keyword, revisit the article and re-optimize it for the new keyword. For example, strategically incorporating the new keyword in the title could significantly boost organic traffic.
- Maintaining a healthy website: Conduct regular website assessments, both holistically and on a page-by-page basis, to ensure it’s fully optimized for Google and other search engines. For a head start, use our free website grader for an instant SEO and online presence audit. There you have it—your SEO Content 101 guide. As previously mentioned, feel free to leave your questions about creating and optimizing content for SEO in the comments section. Hungry for more? Explore additional tips for all your content creation needs, encompassing SEO, social media, and landing page optimization.