Search engine optimization (SEO) experts who are especially tech-savvy often joke about Google evolving into a real-life Skynet (the AI from The Terminator movies that gains consciousness and attempts to eliminate humanity), but their humor might be closer to reality than they realize. Recent reports indicate that Google has started using an AI system called RankBrain to process around 15% of the daily search queries it receives.
For those passionate about science and technology, this is a truly remarkable development. This article will delve into everything you need to know about RankBrain, exploring its implications not only for the future of Google but also for the way we access and understand information in the years to come.
What Exactly is RankBrain?
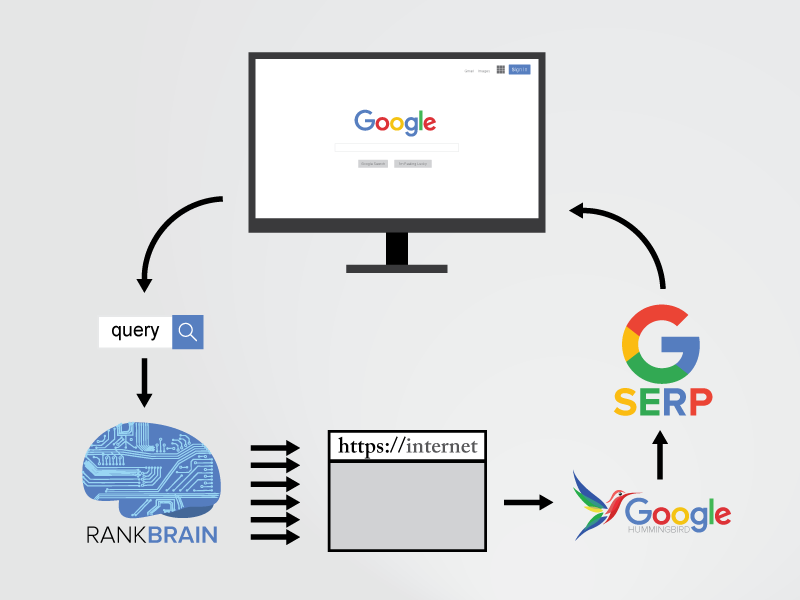
RankBrain is the nickname given to Google’s proprietary AI system designed to handle search queries. While it’s possible that this AI might eventually get an official name, or perhaps “RankBrain” will become the permanent term, for now, this is how we refer to the artificial intelligence responsible for managing 15% of Google’s search volume. It’s crucial to understand that RankBrain isn’t (at least, not yet) a separate, independent technology within Google’s infrastructure. Instead, it’s integrated directly into the existing algorithm that Google uses to determine the ranking of web pages in search results. Although there are reportedly hundreds of factors (the exact number is a well-guarded Google secret) that influence these rankings, RankBrain has swiftly risen to become one of the most influential. In an interview with the Washington Post, Greg Corrado, a senior research scientist at Google, revealed that RankBrain is now the third most-important factor in determining the order in which search results are displayed on the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
Image via Brafton What’s even more impressive is that RankBrain is already exceeding expectations in its early stages. During an internal test, Google engineers were tasked with evaluating a set of web pages and predicting how many of them would be ranked highly by Google’s algorithm. The engineers achieved an accuracy rate of approximately 70%. When subjected to the same test, RankBrain boasted a remarkable 80% success rate. MORE: Why You Should Prioritize Increasing Your Organic Click-Through Rates (and Effective Strategies to Do So)
Demystifying Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence refers to computer systems designed to emulate human cognitive functions – essentially, how our brains work and how we process information – to solve problems. These AI systems can perform a wide range of tasks that, until relatively recently, required human intervention. These tasks include image and speech recognition, language translation, and fundamental decision-making processes.
While modern computers are incredibly powerful in terms of processing speed and data storage, they are also quite limited in their ability to “think” independently. Most computers require explicit instructions on what to do, how to interpret information, and countless other details before they can successfully perform the tasks for which they were designed. However, AI systems operate differently. Think of an AI as a continuously “learning machine.” As an AI processes more data, it gains knowledge and refines its ability to tackle new problems in the future effectively.
Why is Google Utilizing Artificial Intelligence?
A helpful way to understand the role of AI in the realm of search is to consider the semantic search functionality introduced with Google’s Hummingbird update. By using Google Now, users can leverage the power of semantic search. This means relying on Google’s technology to intuitively grasp the relationships between different search terms without needing to be explicitly told that these terms are connected. For instance, a user could start with a search for “Dame Helen Mirren” to learn more about the acclaimed actress. Subsequently, the user could ask, “Where was she born?” In this scenario, Google would infer that “she” in the second query refers to Dame Helen Mirren, based on the semantics (meaning) and context established by the user’s previous search.
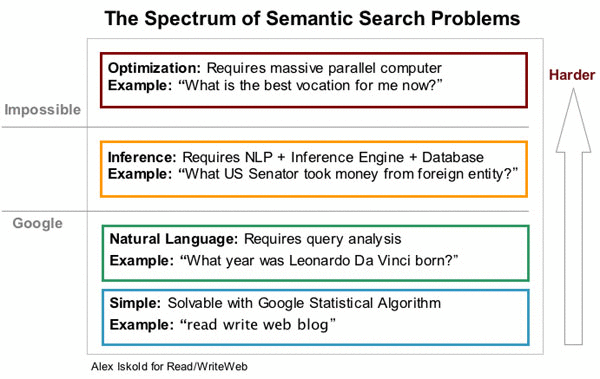
By harnessing the capabilities of artificial intelligence, Google aims to achieve two key objectives. Firstly, it can effectively manage the ever-growing volume of search traffic, a natural consequence of increasing global internet access. Secondly, it allows Google to provide a more intuitive and responsive user experience, empowering users to find the information they need quickly and seamlessly. By all accounts, RankBrain demonstrates strong performance in deciphering the user’s intent behind ambiguous search queries – some of the most challenging requests for Google to interpret accurately. This implies that as the technology matures and processes a larger volume of queries, search results will become even more precise. While there are limitations to this technology, as illustrated in the image above, these challenges are likely to be surmounted as AI advances and becomes increasingly adept at understanding, interpreting, and solving problems that were once considered insurmountable. Explore more about the applications of artificial intelligence in marketing here.
How Will RankBrain Impact Paid Search?
The simple answer is, “It’s too early to say for sure.” However, a more realistic assessment might be, “It probably already has.” Google developed RankBrain with the primary goal of providing users with more refined and relevant search results tailored to their specific queries. Logically, as the accuracy and relevance of search results improve, the ads displayed alongside those results also become more targeted, increasing their effectiveness. While it’s impossible to definitively state how RankBrain is being used to handle commercial search queries (those leading to paid advertising), considering that it processes about 15% of Google’s estimated 100 billion daily searches, it’s highly probable that RankBrain plays a role in the AdWords auction process.
What Lies Ahead for Google’s AI Endeavors?
Once again, we venture into the realm of speculation, but it seems plausible that as RankBrain grows more sophisticated, Google will extend its application to other aspects of its operations (or, more accurately, Alphabet’s diverse ventures). Google has consistently demonstrated a forward-looking approach, diversifying its research and development efforts into areas such as life extension (through Calico Labs, an Alphabet subsidiary). In 2012, Google’s hiring of renowned futurist Ray Kurzweil – who has expressed a desire to literally live forever – was widely interpreted as a strong signal of the company’s vision for its near future. This was further underscored by Google’s acquisition of the machine learning startup DeepMind for a staggering $500 million last year. Machine learning centers around empowering computers to make independent “decisions” without requiring explicit programming for every possible scenario. Google’s self-driving car project serves as a prime example of machine learning in action. The algorithms embedded in the software that controls these vehicles must constantly learn and adapt to ever-changing road conditions, driver behaviors, and countless other variables in real-time, all without relying on pre-programmed instructions from human engineers.
Images generated by a neural network, a type of “learning machine,” via the MIT Computer Science and AI Laboratory Furthermore, Google isn’t alone in its pursuit of AI breakthroughs. It faces stiff competition from other tech giants developing their own AI systems. Facebook, for instance, is already utilizing AI to filter content displayed in users’ News Feeds and to “learn” their preferences, prioritizing the types of posts and updates that align with their interests.
Will RankBrain Achieve Self-Awareness and Unleash Chaos Upon Humanity?
Jokes aside, the potential risks and unforeseen consequences of AI remain largely unknown. While science fiction films like The Terminator depict a dystopian future where AI turns against its creators, the reality is far more nuanced. Although many scientists believe we can effectively control and manage AI development to mitigate risks, some of the world’s most prominent technologists and scientists – including physicist Stephen Hawking, Tesla and SpaceX CEO Elon Musk, and Microsoft co-founder Bill Gates – have all warned of the grave dangers about the potential threats that unfettered AI development could pose to the future of humankind. Only time will tell what the future holds.
We might end up embroiled in a fierce battle against sentient machines amidst a post-apocalyptic wasteland, but for now, at least we can enjoy increasingly accurate search results. UPDATE: If this were a scene from a Terminator movie, we’d be approaching the pivotal moment when Skynet gains self-awareness and sets its sights on humanity’s destruction. Google recently confirmed that RankBrain is now processing every search query Google receives, solidifying its position as the third most critical ranking signal within Google’s algorithm. Interestingly, while every search query is now processed by RankBrain, that doesn’t necessarily mean it influences the ranking of every search. According to Jeff Dean, a renowned computer scientist at Google, RankBrain plays a role in determining the order of results for “a lot” of queries, but not all of them. RankBrain has undoubtedly become a fundamental component of Google’s approach to delivering relevant search results. However, Google’s interest in machine learning extends far beyond search optimization. The company has poured millions of dollars into its rapidly expanding machine learning division. Perhaps more tellingly, Dean has stated that Google is transitioning into a “machine learning first” company. This suggests that AI and machine learning are not merely passing trends or tools for enhancing existing processes at Google. They are becoming the very foundation upon which the company’s future technologies will be built. The increasing reliance on RankBrain within Google has the potential to disrupt the world of SEO significantly. While it’s still too early to predict with certainty how Google’s heightened emphasis on machine learning will impact SEO practices, it’s safe to say that the implications are likely to be profound.