If your website has broken links, it can negatively impact all the effort you’ve invested in making it a valuable resource. Broken links result in a poor user experience, causing frustration and potentially driving visitors away. Moreover, they harm your SEO efforts by hindering the flow of link equity and negatively impacting your search engine rankings. Regularly checking for and fixing broken links is essential. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you through the process:
Step 1: Finding Broken Links
Various tools, including free options, can help identify broken links on your website.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics, a powerful tool for tracking website performance, can also easily identify broken links:
- Log into your Google Analytics account and navigate to the Behavior tab.
- Select “Site Content” and then “All Pages.”
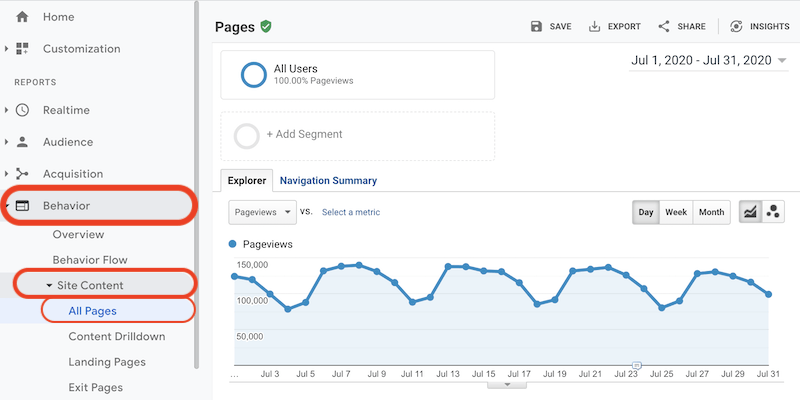
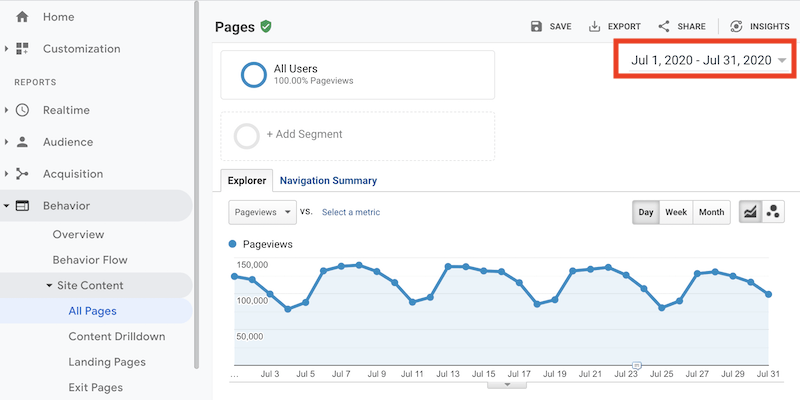
- Set the evaluation period to the desired timeframe for analysis, such as the time elapsed since your last check. For instance, if you check monthly, set the period for the previous month.
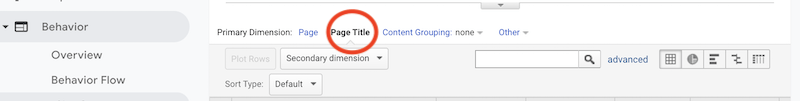
- Under viewing options, ensure you select “Page Title” instead of the default “Page” setting.
- Create a page title filter by clicking on the “advanced” option.
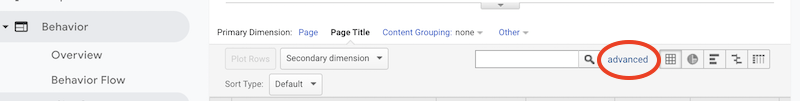
- In the “advanced” window, configure your filter to include page titles containing your 404 error page title.
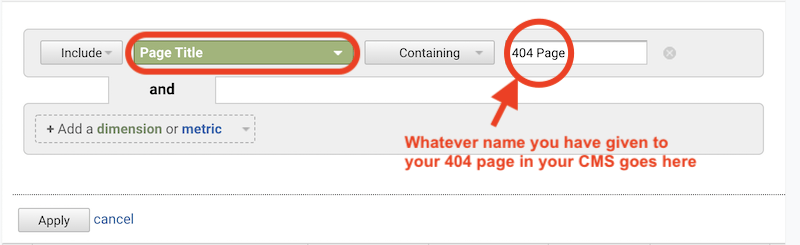
- After applying the filter, you’ll see a list of page titles matching your criteria. The number of results will depend on your chosen timeframe.
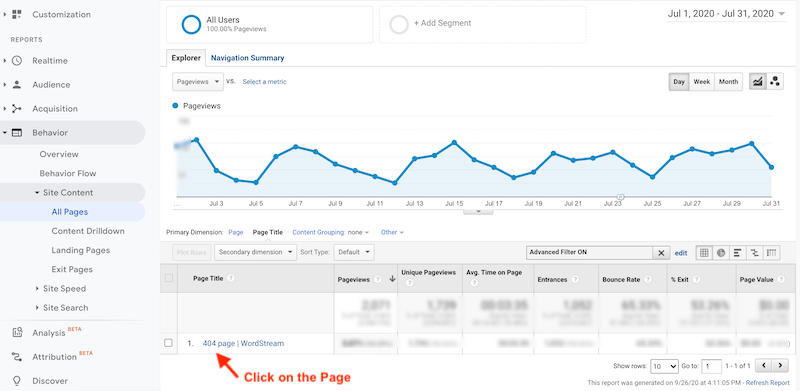
- Clicking on a page title will reveal the broken links leading to the 404 page.
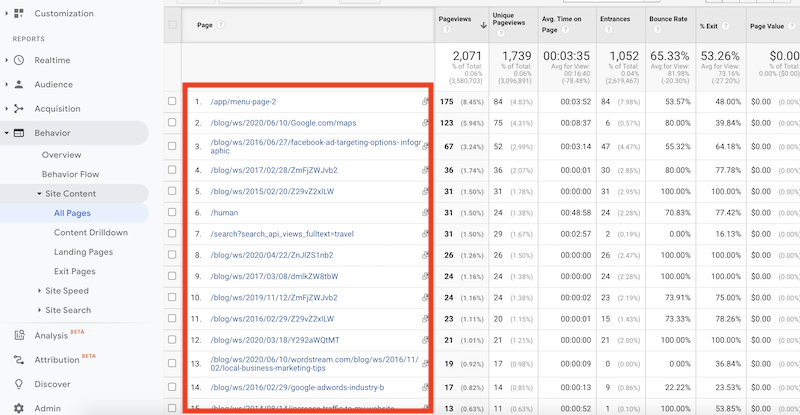
- In the full-screen view, you can observe the total occurrences of the 404 error and the number of pages from which it originated at the top and bottom, respectively.
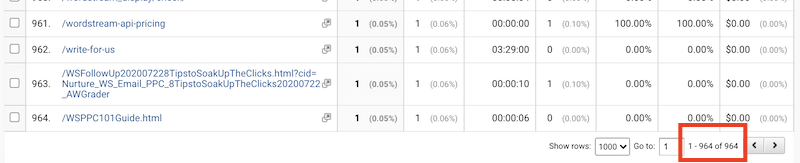
You have the option to export this report to a spreadsheet and address the broken links by either directly fixing them or implementing redirects to the appropriate pages. Any nonexistent or broken links will result in a 404 error page. While most websites display a simple message, best practices suggest providing visitors with a clear course of action, such as links to your homepage, blog homepage, or contact page.
From our blog post on examples of great 404 pages.
Google Analytics allows you to set up email alerts for regular broken link reports and export detailed information. Keep in mind that managing broken links is an ongoing process. A monthly check is a good practice for most websites.
Xenu
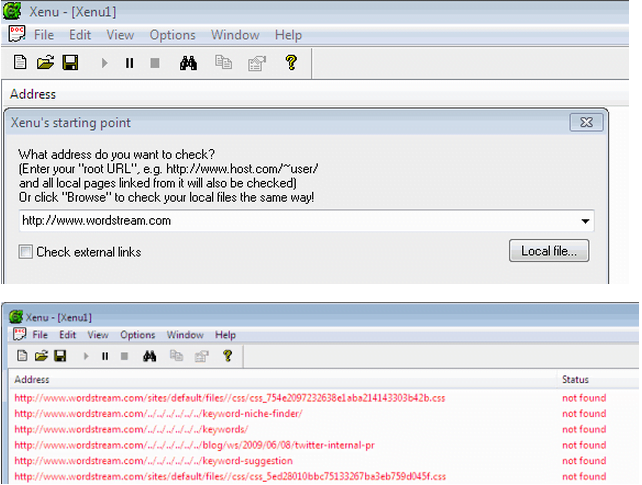
Another recommended free tool is Xenu Link Sleuth. After installing and opening the Xenu software, follow these steps:
- Go to File > Check URL and input your website’s domain.
- Uncheck “check external links”.
- Click “OK” to initiate the analysis. Note that the initial report generation might take some time.
Step 2: Creating a Report and Tracking Changes
After identifying broken links, create an Excel spreadsheet, such as “Broken Link Redirect Report,” to track the redirect process. Export the Google Analytics report as a CSV for Excel, focusing on columns related to broken links, page views, and unique page views. Similarly, export data from Xenu by going to File > Export to Tab Separated File, and open the text file in Excel. Organize the data from Google Analytics and Xenu into separate sections within your Excel spreadsheet.
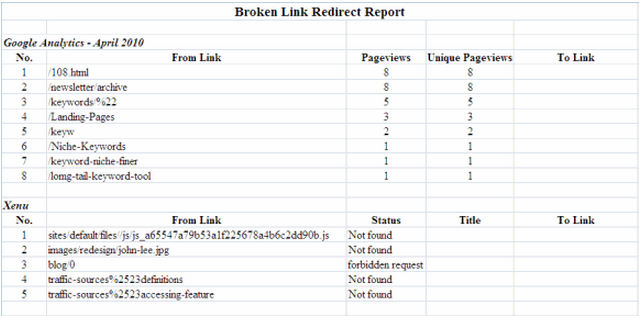
Step 3: Analyzing Data and Deciding Redirection Strategy
This step involves analyzing the identified broken links and determining appropriate actions. Not all broken links require immediate attention. Analyze page views and the reasons behind broken links to prioritize your efforts. In Google Analytics, some broken links might have significantly higher visits than others. Prioritize fixing links with multiple visits as they indicate a recurring issue. You can easily determine the correct URLs for some links while others might require a tentative URL (highlight for easy identification). For remaining links, redirecting to the domain homepage is an option. Focus on redirecting links with high traffic and those resulting from identifiable errors. The Xenu report helps identify broken links present on your site, excluding those arising from typing errors. However, even these URLs might contain errors. Analyze the report for patterns in errors, such as character replacements, and address the root cause. This step concludes with documenting all links requiring redirection in your Broken Link Redirect Report.
Step 4: Implementing Redirects in CMS
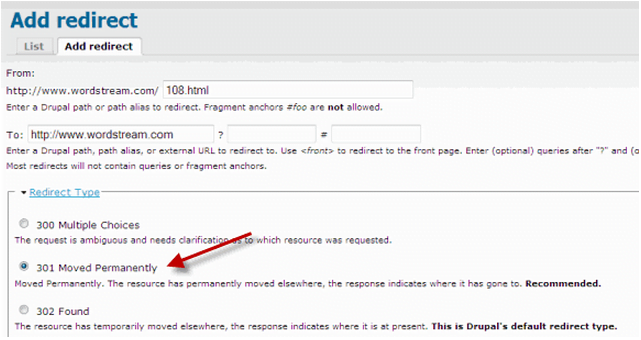
This stage involves redirecting broken links within your content management system (CMS). Using nexus-security’s Drupal CMS as an example:
- Navigate to Administration > Site building > URL redirects.
- Click “Add redirect.”
- Copy and paste the “From” and “To” URLs from your Broken Link Redirect Report.
- Choose “301 Moved Permanently” from the Redirect Type menu.
- Click “Create new redirect.”
Repeat these steps to redirect all documented broken links, updating your report accordingly. By ensuring all your links are functional, you enhance your website’s user experience and improve its performance in search engine results.