Google utilizes structured data found on websites to comprehend page content and gather insights about the web and the world at large. For instance, let’s examine a JSON-LD structured data snippet that might be present on the contact page of the Unlimited Ball Bearings company. This comprehensive guide will delve into the realm of structured data and how to effectively use schema for SEO purposes.
You might have come across terms like structured data, Schema.org, and JSON-LD. But what exactly do these terms mean exactly? What is the purpose of schema.org? How do structures function? And what is their connection to SEO? This is for those who are unfamiliar with structured data.
Understanding Structured Data
Structured data is essentially code implemented on your website. It adheres to a specific format, making it comprehensible to search engines. Search engines read the code and leverage it to present search results in specific ways.
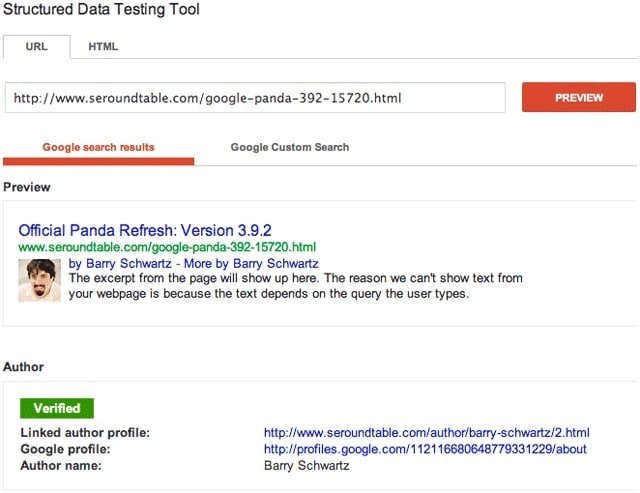
Imagine having a website dedicated to recipes. By incorporating structured data into a recipe page, you enhance its visibility in search engine results, making it “richer” in terms of displayed content. This is why these results are referred to as “rich snippets.” Here’s a visual representation:
Apart from the title, URL, and search result description, you can see the estimated preparation time for the “absolute best lasagna” and its calorie count. To achieve such a rich snippet, you must incorporate structures into your web page using an SEO guide that focuses on schema.
There’s a wide array of structured data, all formatted as code. Whether it’s for books, reviews, movies, or products, structures provide additional details to your search result snippets.
However, it’s important to note that Google doesn’t always generate a rich snippet for your page, even with structured data implemented. There’s no guarantee. Your best bet is to add it and hope Google picks it up!
The Purpose of Structured Data
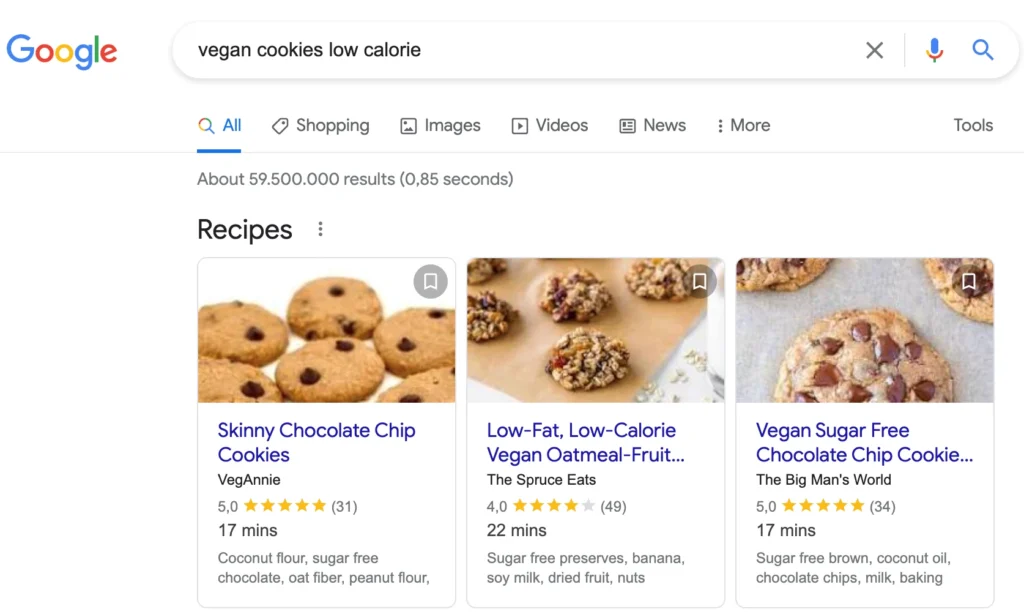
Structured data enables communication with search engines, allowing you to convey specific details about your content. For instance, you can specify the ingredients in a recipe, the preparation time, and the calorie count. Google instantly processes this information and may choose to display it in search results.
Essentially, it’s a tool for conveying detailed page information to Google in a way it understands. Google can then use this information to create informative and engaging rich snippets, which are highly appreciated by audiences.
Exploring Schema Markup Types
The schema.org vocabulary encompasses formats for structuring data related to people, places, and things on the web. A comprehensive list of elements definable by Schema markup is available on the Schema website.
Pattern tags are commonly used to denote:
- Reviews
- Events
- Articles
- Products
- People
- Organizations
- Local Businesses
- Recipes
- Medical conditions
- FAQs
Integrating these tags into your website helps search engines understand its content and present this information through rich snippets, making it a valuable tool for SEO.
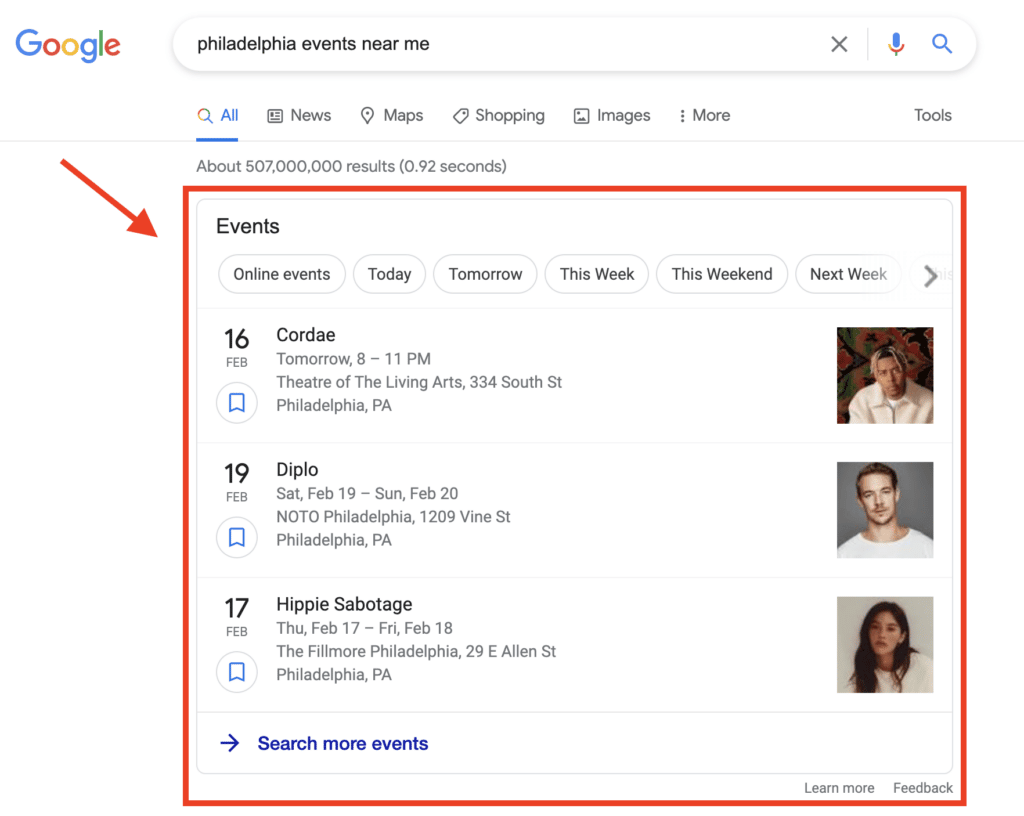
For example, observe the results for a page implementing event-pattern tagging; you can see the dates and locations of various tagged events. Here’s an example of a rating-rich snippet resulting from the schema:
Delving into Creative Works
Creative Works is a prominent branch of pattern vocabulary, serving as an awards repository for creative content like movies, books, video games, and music.
Consider this result with the “movie” tag, showcasing movie-specific details like rating, genre, and theatrical release date.
These tags can be implemented using various coding languages, including RDFa, Microdata, and JSON-LD.
Understanding schema.org
Major search engines have collaboratively developed a project called Schema.org.. This platform provides a comprehensive collection of structured data markups supported by these search engines, making it an invaluable resource for website SEO.
You can utilize Schema.org to find the markup tailored to your specific page. For instance, if you sell t-shirts on your website, you can use schema to display available colors and sizes in your search snippet. Explore Schema.org/Product to discover the possibilities.
Schema.org offers code examples for reference. After copying the code, you need to adapt it to your specific requirements.
It’s important to note that Schema.org represents a taxonomy of code formats understood by major search engines and provides code examples. Other forms of structured data exist, such as Open Graph (used by Facebook) and Twitter cards (used by Twitter).
Demystifying JSON-LD
JSON-LD is one of the Schema.org markups, essentially a way to write code. Schema.org also offers other markups, such as Microdata and RDFa. Yoast recommends using JSON-LD because it’s less likely to disrupt your site’s functionality compared to other markups. Moreover, JSON-LD can be easily added to your website using Google Tag Manager, which isn’t possible with other markups.
Understanding Microdata
microdata implementation shares similarities with RDFa, and its properties include:
- itemscope: Creates an item and indicates that the subsequent content provides information about it.
- itemtype: Describes items and properties using a valid vocabulary URL (e.g., “https://schema.org”).
- itemprop: Specifies a value within a tag, representing a specific item property (e.g., itemprop=“name”).
- itemid: Represents the unique identifier for the specified item.
- itemref: Refers to item properties located outside the item’s scope, providing a list of item IDs and other properties elsewhere in the document.
Exploring Resource Description Framework in Attributes (RDFa)
RDFa properties encompass:
- about: Specifies the resource the metadata refers to.
- rel and rev: Indicate a relationship and its reverse connection with another resource.
- src, href, and resource: Determine partner resources.
- content: Overrides the element’s content when using the property attribute.
- datatype: Restricts the data type of text used with the property attribute.
- typeof: Specifies the RDF type of the subject or partner resource.
The Significance of Structured Data for SEO
Structured data is crucial for SEO because it helps Google understand your pages and website content more effectively. Google needs to determine a page’s content to display it appropriately in search results. Structured data facilitates this understanding by explicitly conveying your website’s content.
Furthermore, structured data enhances your search snippet by displaying more information to users, such as specific information. This increased visibility can lead to higher click-through rates, ultimately boosting your rankings.
Implementing Structured Data
While using structured data might sound complicated, it’s manageable with the right guidance. It involves obtaining the correct code, adapting it to your needs, and using Google Tag Manager to implement it on your site.
Numerous resources, including posts on Schema.org and JSON-LD, are available to deepen your understanding of this subject.
Leveraging Plugins for Structured Data
Many structured data markups can be easily added to your website using plugins. For example, a local SEO plugin utilizes structured data to display your store’s location(s). This eliminates the need for manual coding; simply install the plugin, provide the necessary details, and let it handle the rest. Numerous other plugins can help you use this technique without dealing with complex code.