It’s impossible to avoid big data in today’s business landscape. This tutorial offers a glimpse into the world of big data, its relevance, and how to leverage it using the Twitter API and Python.

What is Big Data?
Big data is simply massive amounts of data. A single data point might not be insightful, but terabytes of data processed with complex algorithms and powerful computers can reveal insights beyond human capabilities. Big data analytics offers invaluable benefits, constantly pushing the boundaries of human understanding.
The initial step is “data mining,” the process of gathering data. Businesses handle vast amounts of user, product, and location data. We’ll explore data mining techniques to collect Twitter data, which can be surprisingly useful.
Imagine Facebook using Messenger data to enhance advertising strategies. Messenger handles 1.2 billion monthly active users. Here, the big data comprises user conversations. Analyzing individual conversations can provide insights into user preferences, enabling targeted product recommendations. With Natural Language Processing (NLP), this analysis can be automated on a massive scale.
This example highlights the value of machine learning and big data analytics for businesses.
Why Twitter Data?
Twitter is a data goldmine. Unlike other platforms, most tweets are public and accessible, making it perfect for large-scale analysis. Twitter’s API enables targeted queries, like retrieving tweets about a specific topic within a timeframe or gathering a user’s non-retweeted tweets.
One application could be gauging public perception of your company. You could collect recent tweets mentioning your company and perform sentiment analysis.
We can also target users geographically using spatial data. Imagine mapping global areas where your company is mentioned most frequently.
Twitter data offers a window into public opinion and topic perception. Its accessibility and generous API rate limits make it a powerful tool.
Tools Overview
We’ll use Python 2.7, preferably within an IDE like PyCharm - Community Edition.
We’ll access Twitter’s API using the Python library Tweepy, which we’ll install shortly.
Getting Started
Twitter Developer Account
To use Twitter’s API, create a developer account on the Twitter apps site:
Log in or create a Twitter account at https://apps.twitter.com/.
Create a new app (top right button).

Provide a unique app name, website (placeholder is fine), and project description. Accept terms and conditions.
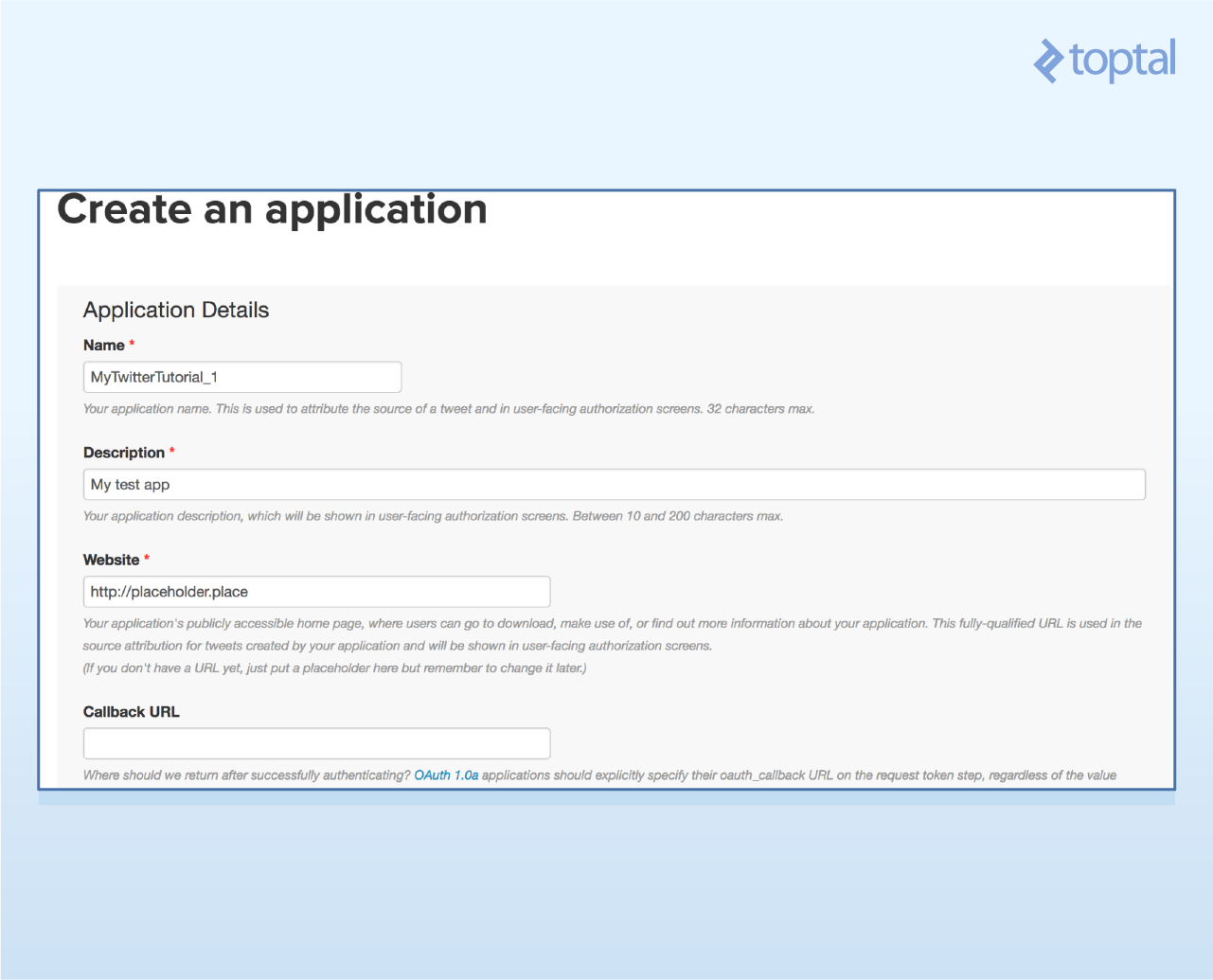
Go to “Keys and Access Tokens” to find your consumer key and secret.
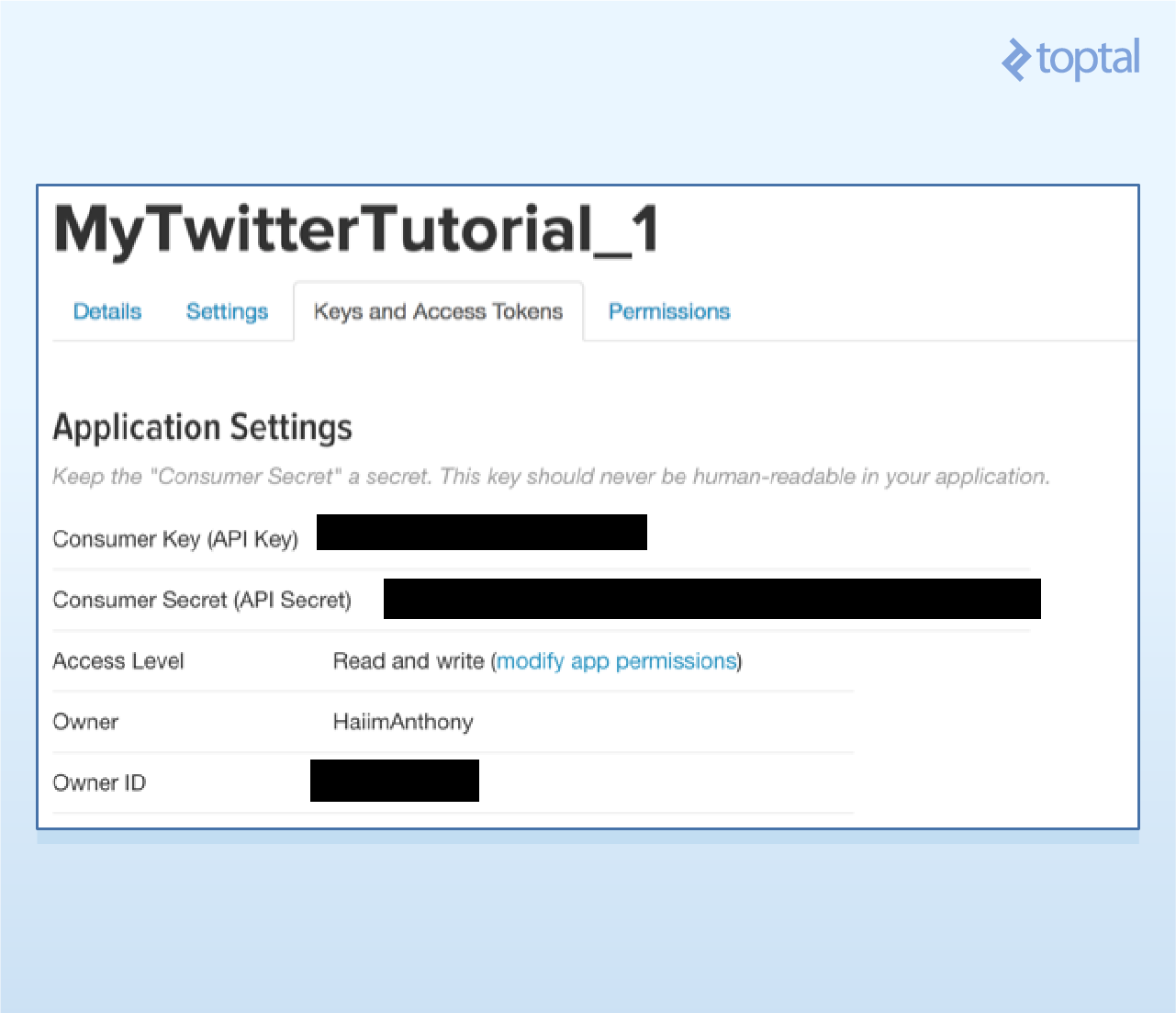
Scroll down, request access tokens, and note your access token and secret after the page refreshes.

Save these credentials for later use.
Installing Tweepy
Tweepy is a robust library for accessing the Twitter API, supporting various Python versions. You can install it using pip or GitHub.
Using Pip
Type pip install tweepy in your terminal.
Using GitHub
Follow the instructions on Tweepy’s GitHub repository. The steps are:
| |
Troubleshooting information is available there.
Authentication
With tools ready, let’s start coding! Each application requires using Tweepy to create an API object for calling functions. First, authenticate using your developer information.
Import Tweepy and add your credentials:
| |
Create the API object:
| |
This object is fundamental, so keep it safe.
Example 1: Your Timeline
We’ll retrieve your ten most recent tweets using the home_timeline() function. Store the result and iterate through it to print the tweets.
| |
The output will display tweets followed by their URLs.

Clicking a link usually leads to the tweet. For instance:
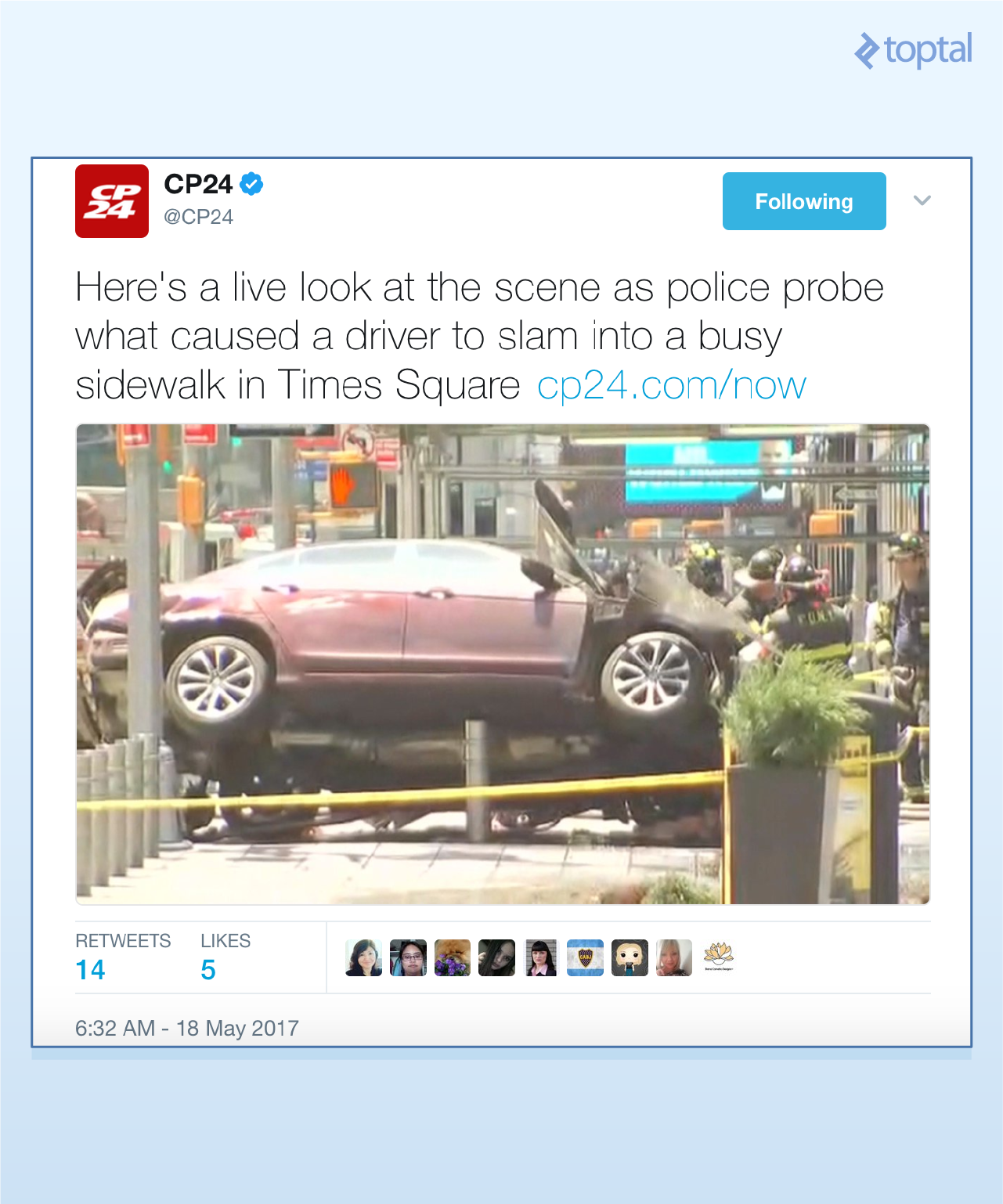
Formatting might differ in the terminal compared to an IDE like PyCharm.
The JSON Behind the Results
We printed tweet text using tweet.text. To access specific attributes, we examine the JSON returned by the Twitter API.
The API response is in JSON format, containing a wealth of information. We’ll focus on the “text” attribute and tweeter information. Refer to here for the complete JSON response.
Here are some tweet attributes:
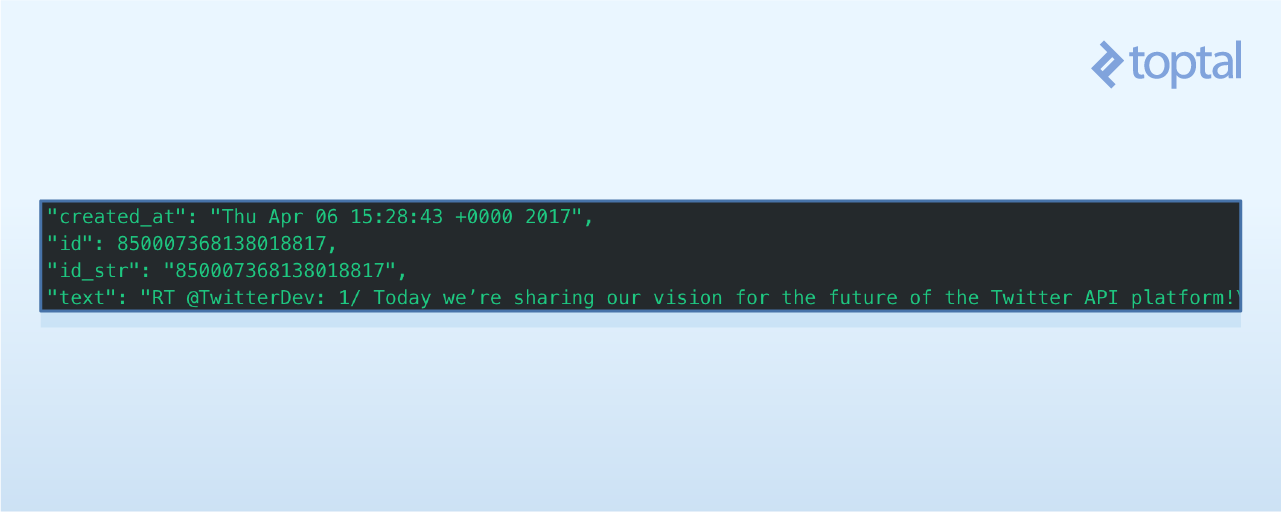
To get the tweet creation date, use print tweet.created_at.
Each tweet object also includes tweeter information:

To access the tweeter’s name and location, use print tweet.user.screen_name and print tweet.user.location, respectively.
These attributes are particularly useful for applications involving spatial data.
Example 2: Tweets from a Specific User
Let’s retrieve the latest twenty tweets from a specific user.
The Tweepy documentation reveals the user_timeline() function.

It has useful parameters like id (user ID) and count (number of tweets). Note that Twitter’s rate limits limits the number of tweets per query.
Let’s fetch the twenty most recent tweets from @NyTimes.

Create variables for tweet count (count) and username (name), then call user_timeline() with these parameters. Remember to keep the authentication and API object creation code.
| |
The output will resemble this:
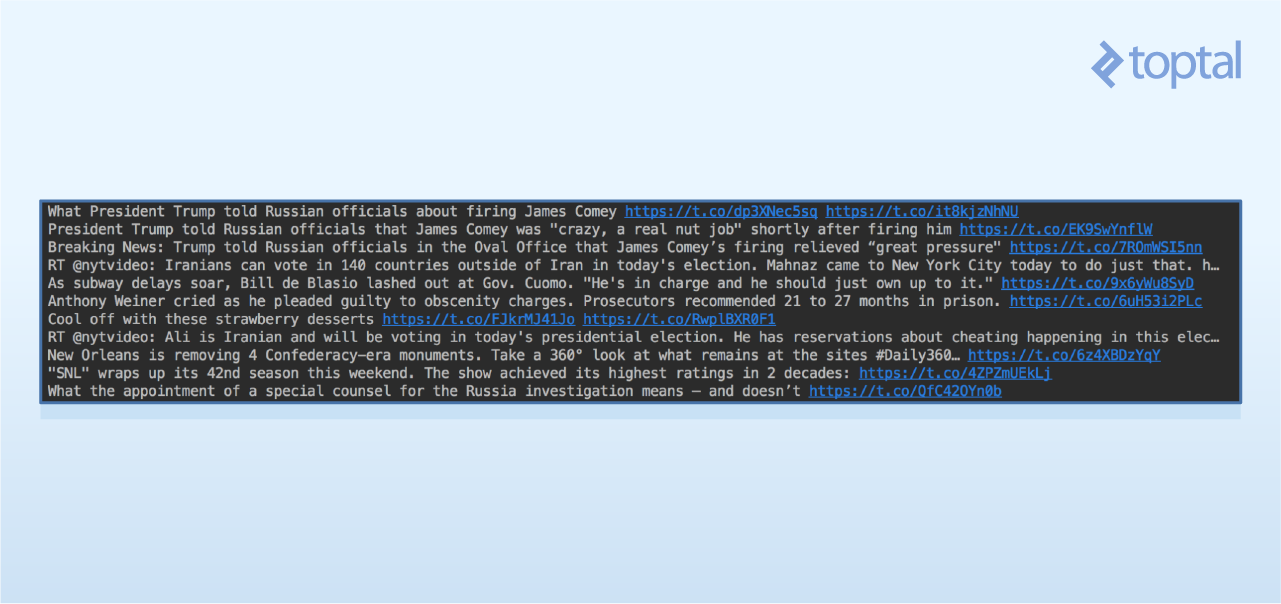
This data enables applications like:
- Analyzing specific users and their interactions.
- Identifying Twitter influencers and studying their followers.
- Monitoring changes in a user’s followers.
Example 3: Finding Tweets Using a Keyword
Finally, let’s retrieve recent tweets containing a specific keyword. This is valuable for monitoring topic mentions or gauging public sentiment about your business. Let’s see how Twitter users are mentioning Toptal.
The Tweepy documentation points us to the search() function.

The key parameter is q (the keyword). We can also set the lang parameter to filter by language. Let’s retrieve English tweets only (“en”).
Modify the code to incorporate these changes. Create variables for the query and language, then call search() through the API object. Print the tweet text and the tweeter’s screen name.
| |
The output will resemble this:

Practical applications include:
- Mapping global locations where your company is mentioned most.
- Performing sentiment analysis on tweets to assess public opinion.
- Creating social graphs of prominent users mentioning your company or product.
We’ll explore these topics in future articles.
Conclusion
Twitter’s API is a powerful tool for data mining and gaining insights into public opinion. For further exploration, delve into the Twitter API, Tweepy, and Twitter’s Rate Limiting guidelines.
We’ve covered the basics of accessing and retrieving data. Twitter’s API can be leveraged for complex big data problems involving social dynamics that are too intricate for human analysis alone.