In July of 2020, a hacker exploited Twitter’s internal systems to gain control of several high-profile accounts, including 130 high-profile Twitter accounts, and used them to perpetrate a bitcoin scam.
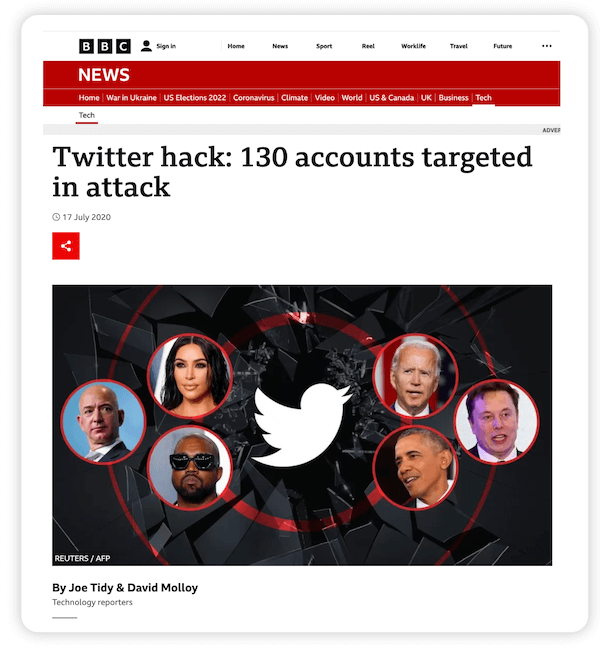 This scheme tricked thousands of Twitter users, resulting in the hacker absconding with over $118,000 worth of bitcoin in a matter of hours. This incident is not isolated. Since then, countless organizations, ranging from giants like Apple and Facebook to institutions like universities, hotels, hospitals, government agencies, and even churches and fundraising platforms, have fallen victim to data breaches.
This scheme tricked thousands of Twitter users, resulting in the hacker absconding with over $118,000 worth of bitcoin in a matter of hours. This incident is not isolated. Since then, countless organizations, ranging from giants like Apple and Facebook to institutions like universities, hotels, hospitals, government agencies, and even churches and fundraising platforms, have fallen victim to data breaches.
The truth is, if your organization handles customer data—collecting, processing, or storing it—it’s vulnerable. Therefore, taking immediate action to safeguard this data is non-negotiable. This article will guide you through the necessary steps.
Table of contents
- The importance of data privacy
- Data privacy regulations & standards to know
- The biggest threats to data privacy & data security
- 10 best practices to protect your customer data
The importance of data privacy
Data privacy measures have three primary objectives: safeguarding information confidentiality and integrity, fostering customer trust, and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations. Neglecting these measures can lead to breaches, resulting in dire consequences for both individuals and organizations.
Impact on individuals
When personal data is compromised, individuals become susceptible to victims of identity theft and other fraudulent activities. Perpetrators may leverage this stolen data to impersonate victims, opening credit lines, applying for loans, and engaging in other malicious acts. Furthermore, the loss of sensitive or private information can expose victims to humiliation, discrimination, financial setbacks, and psychological distress. In extreme cases, their well-being, safety, or even their families could be jeopardized.
Impact on organizations
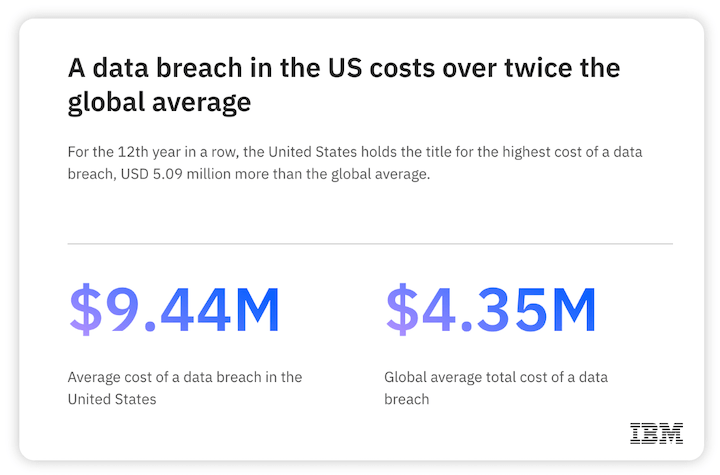
Data breaches inflict significant harm on organizations, particularly financially. IBM reveals that the average cost of a breach has escalated to $4.35 million in 2022. These costs encompass ransom payments demanded by attackers, “cleanup costs” associated with breach remediation and forensic investigations, as well as potential regulatory fines and legal repercussions. Furthermore, a breach can severely tarnish a company’s reputation, erode customer trust, and negatively impact stock prices. The loss of customer confidence and struggles to fulfill contractual obligations can strain business relationships and ultimately impact profitability.
Data privacy regulations & standards to know
In response to the surge in data breaches in recent years, governments worldwide have implemented data privacy laws. These laws regulate how organizations collect, process, store, and dispose of consumer data, aiming to protect consumer privacy and mitigate the damaging effects of breaches.
GDPR
The GDPR applies to any company operating in any country that gathers data from EU residents, governing how they collect, utilize, transfer, and secure this data. Organizations failing to comply with this law risk substantial fines, potentially exceeding $20 million or 4% of their total global revenue.
U.S. data privacy laws
In contrast to the EU, the USA lacks a single, comprehensive federal data privacy law. Instead, a patchwork of sector-specific and state-level laws governs how organizations manage consumer data. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), for instance, focuses on safeguarding protected health information (PHI). Similarly, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) regulates how entities collect and handle personal information of California residents.
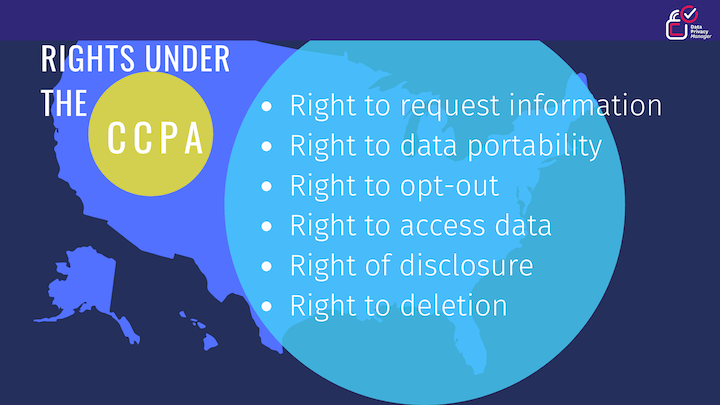 Image source
Utilizing cookie consent banners can be instrumental in ensuring compliance with both GDPR and CCPA. Explore prime examples here.
Image source
Utilizing cookie consent banners can be instrumental in ensuring compliance with both GDPR and CCPA. Explore prime examples here.
Industry-specific privacy standards
Certain industries have established privacy standards through their respective governing bodies. The PCI-DSS, for instance, applies to all merchants globally that handle consumer credit card information. While not legally mandated, adherence to this standard is often a contractual obligation for merchants collaborating with credit card companies. Its objective is to ensure businesses implement adequate safeguards to protect cardholder data and prevent credit card fraud. The tech and advertising sectors have witnessed significant changes in recent years, all in the name of privacy. For example, Google has reduced the visibility of search terms in their reports, and Facebook now mandates Aggregated Event Measurement.
The biggest threats to data privacy & security
Data privacy focuses on regulating the collection, sharing, and use of data, while data security concentrates on shielding data from external threats and malicious insiders. Although distinct, these concepts significantly overlap. Moreover, various threats can compromise both data privacy and security.
Phishing scams
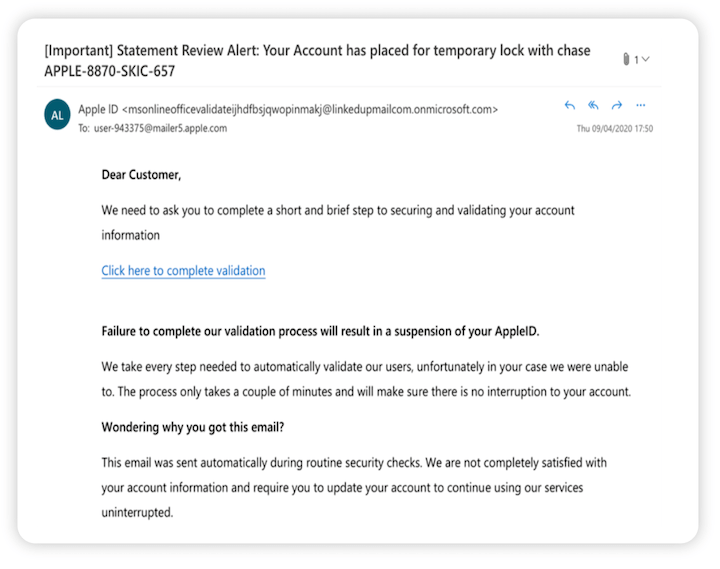
Phishing scams involve attackers sending deceptive emails disguised as communications from trustworthy sources. These emails often contain malicious links or attachments. Clicking such links redirects users to fraudulent websites designed to harvest sensitive information, leading to data breaches. Opening malicious attachments can compromise devices, potentially granting attackers access to broader enterprise networks and causing extensive damage. Therefore, investing in a robust anti-phishing solution tailored to your business is crucial.
Malware and ransomware
Malware and ransomware represent substantial threats to both data security and privacy. In a ransomware attack, cybercriminals infect corporate devices with malware that encrypts systems, denying users access. To regain control, organizations are coerced into paying a hefty ransom in exchange for the decryption key. Many ransomware variants can propagate across networks, exfiltrating vast amounts of sensitive data.
Insider threats
Insider threats pose a significant risk to data privacy. Since 2020, insider incident frequency has surged by 44%, with the average cost per incident escalating to $15.38 million. These threats can stem from malicious or compromised insiders like employees or third-party vendors. Alternatively, they can arise from unintentional actions of careless insiders with poor cybersecurity practices. Sharing passwords with colleagues or storing sensitive information in public folders exemplifies such negligence. These oversights can lead to accidental data leaks or unauthorized exposure.
Software vulnerabilities
Security flaws within devices and applications create opportunities for cybercriminals. Attackers exploit these vulnerabilities to infiltrate organizations, compromising or exfiltrating valuable customer data.
10 best practices to protect customer data privacy
Here are ten strategies to safeguard your valuable customer data from cybercriminals and hackers.
1. Know what data you are collecting
Data protection begins with understanding the data itself and its storage locations. Identify the types of customer data collected, their usage, and the parties involved in processing it. Assess the sensitivity of the data, its storage locations, and the circumstances under which it’s shared. Conduct a comprehensive data audit to pinpoint data repositories across the enterprise. Categorize each data type based on sensitivity, use case, and accessibility requirements. Subsequently, compile a data inventory to determine the specific data requiring protection and the applicable compliance regulations.
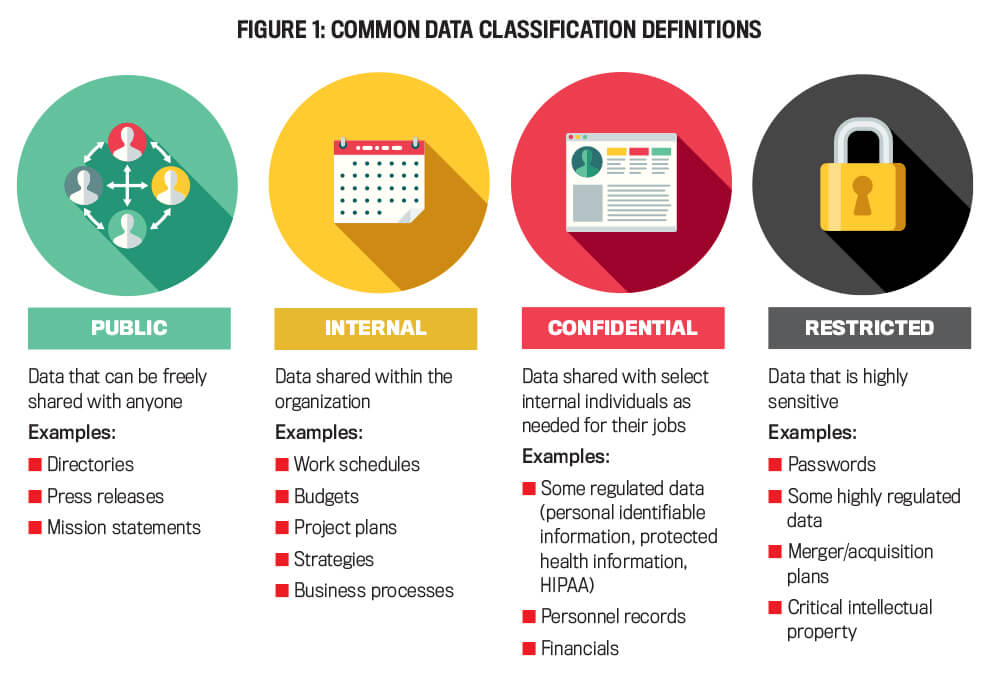 Image source
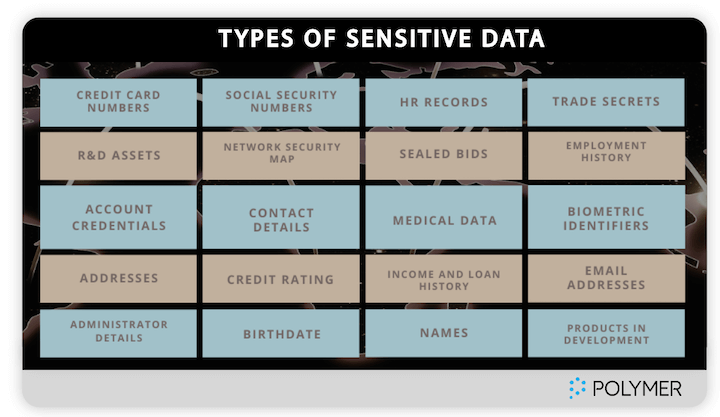
Here’s a breakdown of data classifications:
Image source
Here’s a breakdown of data classifications:
- Public data: This includes press releases, mission statements, and directory listing information.
- Internal data: This encompasses work schedules, budgets, project plans, business processes, strategies, and marketing data.
- Confidential data: This includes personal information, protected health information, personnel records, and financials.
- Restricted data: This encompasses passwords, merger/acquisition plans, and intellectual property.
2. Only collect essential information
Minimizing the potential damage of a data breach can be achieved by limiting the collection of personal data. Focus on gathering only the private or sensitive information essential for specific business objectives, such as enhancing customer experiences and improving retention. Periodic data audits are valuable for evaluating the necessity of collected data. If data isn’t essential, cease collecting it. By doing so, you reduce potential losses in the event of a breach.
3. Create and publish a transparent data usage and privacy policy
Establish a well-defined data privacy policy and communicate it clearly to all stakeholders. This policy should outline who has access to data and under what circumstances. It should also explicitly state permissible and prohibited uses of the data. Moreover, publish a customer-facing privacy policy on your website. This policy should transparently explain how your company collects, stores, utilizes, and safeguards customer data. Keep customers informed of any modifications made to this policy.
4. Encrypt all sensitive user data
Unencrypted and poorly secured data make organizations attractive targets for hackers. Encrypt all data, both during transmission and storage. Employ 256-key bit length encryption for securing data within emails and utilize file-level encryption to protect data residing on systems and servers. Furthermore, establish a routine for regular data backups and store them in secure locations. In the event of a cyberattack, such as ransomware, this practice ensures data accessibility, eliminating the need to pay ransoms.
5. Protect against phishing scams
To mitigate the risk of phishing attacks, implement robust email spam filters measures throughout the organization. Keep all devices updated with antivirus and anti-malware software configured for automatic updates. This proactive approach addresses emerging threats and ensures continuous data protection. Human vigilance plays a crucial role in minimizing the impact of phishing attacks. Encourage employees to report any suspicious emails to the appropriate personnel or department.
6. Update all software
Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in software and devices to infiltrate organizations and compromise customer data. Software vendors release patches to address these vulnerabilities. Therefore, promptly implementing these patches and keeping software up to date are essential for data protection.
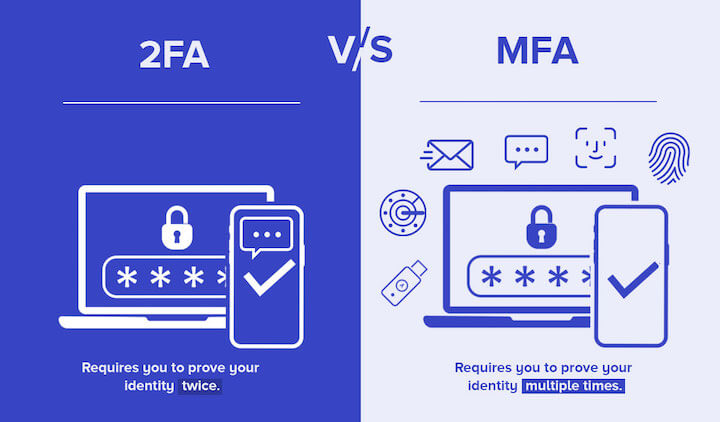
7. Implement multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security to enterprise accounts and sensitive data. MFA requires more than just a password for authentication. Even if a hacker obtains an authorized user’s password, they still need the second factor to access the account. This second factor typically remains in the authorized user’s possession, making it significantly harder for attackers to compromise.
8. Train people about cybersecurity practices
Cybersecurity education is paramount for addressing human-related vulnerabilities. Train employees on best practices and educate them on recognizing signs of phishing attacks and how to avoid social engineering scams. Emphasize the importance of strong passwords and MFA. Additionally, explain the risks associated with using public Wi-Fi networks for work and stress the importance of adhering to the organization’s security and privacy policies.
9. Limit access to data
Limiting data access to a need-to-know basis effectively minimizes internal threats. Adhering to the principle of least privilege (PoLP) is crucial. This principle dictates that users should only have access to the data essential for their roles. Leverage identity and access management (IAM) tools to effectively manage access levels and permissions.
10. Implement a comprehensive data protection infrastructure
A robust security infrastructure is crucial for securing customer data and preventing breaches. This infrastructure should include the following tools:
- Antivirus and anti-malware software
- Anti-adware and anti-spyware software
- Next-generation web firewall
- Pop-up blockers
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools
- Vulnerability scanner
- Password manager
- MFA Allocate a dedicated budget for these security tools. These investments contribute significantly to protecting your organization from data breaches and offer a relatively quick return on investment.
Keep your business, customers & data safe
The digital landscape has witnessed a significant increase in the number and frequency of data breaches, particularly in the past five years, with numerous high-profile organizations targeted, impacting millions of individuals. However, it’s not a hopeless situation. You retain control over the data you collect and utilize. By adopting the strategies and best practices outlined in this article, you can mitigate risks to your company and safeguard valuable customer data.
- Know what data you are collecting
- Only collect essential information
- Create and publish a transparent data usage and privacy policy
- Encrypt all sensitive user data
- Protect against phishing scams
- Update all software
- Implement multi-factor authentication
- Train people about cybersecurity practices
- Limit access to data
- Implement a comprehensive data protection infrastructure