This guide offers a concise walkthrough on developing a secure Node.js GraphQL API.
You might be wondering:
- Why use a GraphQL API?
- What exactly is a GraphQL API?
- What constitutes a GraphQL query?
- What benefits does GraphQL offer?
- Is GraphQL superior to REST?
- Why choose Node.js for this purpose?
These are all pertinent questions. Before delving into those, let’s briefly examine the current web development landscape:
- Virtually every modern solution incorporates some form of application programming interface (API).
- Even using social media platforms like Facebook or Instagram involves interacting with a front-end that consumes an API.
- Online entertainment services such as Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube all utilize different API types.
In essence, APIs are everywhere. While you don’t need to grasp their intricate details or underlying technologies, they enable seamless communication between services using a common standard.
A well-designed API ensures a robust, maintainable, and scalable system capable of serving diverse clients and front-end applications.
So, What Exactly Is a GraphQL API?
GraphQL is a query language for APIs. Initially developed for internal use at Facebook, it was released publicly in 2015. Supporting reading, writing, and real-time updates, this open-source language is often compared to REST and other architectures. Its core principles include:
- GraphQL Queries: Allow clients to read and customize how data is received.
- GraphQL Mutations: Define how data is written to the server, establishing a standard for data writing within the system.
This article aims to provide a practical, real-world example of building and using GraphQL APIs. However, it won’t delve into a comprehensive GraphQL introduction. The GraphQL team offers extensive documentation and best practices in their Introduction to GraphQL.
Understanding GraphQL Queries
As mentioned earlier, queries enable clients to retrieve and manipulate data from the API. You can specify the object type and select the desired fields. Consider this simple query:
| |
This query fetches all users from the “users” schema, but retrieves only the firstName and lastName fields. A possible result might look like this:
| |
The client-side usage is quite straightforward.
Why Use a GraphQL API?
APIs enable software as a service, allowing integration by external services. Even if your application serves a single front-end, that front-end acts as an external service. By communicating through the API, you can work on these components as distinct projects.
Large teams benefit from separate front-end and back-end teams, both leveraging the same technology and streamlining their workflows. When designing an API, prioritize the approach that best suits your project and helps you achieve the desired outcome.
This article focuses on building a skeletal GraphQL API.
Is GraphQL Superior to REST?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. It depends.
GraphQL excels in certain scenarios, while REST, as an architectural approach, has proven effective in many others. Countless articles argue for one over the other, suggesting various implementations.
The key is to understand the strengths of each approach. Analyze your specific solution, consider your team’s expertise, and evaluate their learning curve before making a decision.
This article emphasizes practical guidance rather than a subjective GraphQL vs. REST comparison. For a detailed comparison, refer to our article “GraphQL vs. REST - A GraphQL Tutorial.”
Today, we’ll focus on building a GraphQL API using Node.js.
Why Node.js?
GraphQL boasts several libraries. We chose JavaScript with Node.js due to their popularity and the fact that Node.js allows developers to use familiar front-end syntax for server-side development.
Comparing this approach with a REST-based API, similar to the one demonstrated in our article “Creating a Secure REST API in Node.js,” proves insightful. That article showcases Node.js with Express to develop a skeletal REST API, highlighting some differences between the two approaches. Node.js, designed for scalable network applications, benefits from a large community and numerous open-source libraries found in the npm website.
Today, we’ll build a skeletal API using GraphQL, Node.js, and Express!
Hands-on GraphQL Tutorial
This tutorial outlines the creation of a basic GraphQL API. Familiarity with Node.js and Express is recommended. The source code for this GraphQL example is available here.
We’ll manage two types of resources:
- Users: Handling basic CRUD operations.
- Products: Demonstrating GraphQL’s capabilities with more detail.
User structure:
- id
- firstname
- lastname
- password
- permissionLevel
Product structure:
- id
- name
- description
- price
We’ll be using TypeScript for this project. The source file includes configuration instructions for TypeScript.
Let’s Code!
Ensure you have the latest Node.js version installed (currently 10.15.3, as per Nodejs.org).
Initializing the Project
Create a new folder named node-graphql. Open a terminal or Git CLI console and run: npm init.
Configuring Dependencies and TypeScript
To expedite the process, replace your package.json with the one provided in our Git repository, containing all necessary dependencies:
| |
Run npm install to install all dependencies needed for this GraphQL API within Node.js and Express.
Next, configure TypeScript by creating a tsconfig.json file in your root folder:
| |
The code logic will reside in the “app” folder. Create an app.ts file and add the following code for testing:
| |
With this configuration, running npm start builds the project and allows testing. Your terminal console should display “Hello GraphQL Node API tutorial.” Behind the scenes, TypeScript code is compiled into JavaScript and executed in the build folder.
Now, let’s set up a basic GraphQL API skeleton. We’ll import three essential components:
- Express
- Express-graphql
- Graphql-tools
Putting it all together:
| |
We can start coding now. Let’s set up the Express app and basic GraphQL configuration:
| |
Here’s what we’re doing:
- Enabling port 3000 for our Express server.
- Defining the queries and mutations we’ll use.
- Defining the functionality of those queries and mutations.
Let’s clarify the roles of typeDefs, resolvers, queries, and mutations:
- typeDefs: Define our schema, outlining expectations for queries and mutations.
- Resolvers: Specify the functions and behavior of queries and mutations.
- Queries: Represent “gets” for reading data from the server.
- Mutations: Represent requests that modify data on the server.
Running npm start should now display: “Node Graphql API listening on port 3000!”
We can test our GraphQL API at: http://localhost:3000/graphql
Let’s write our first query, “hello”:
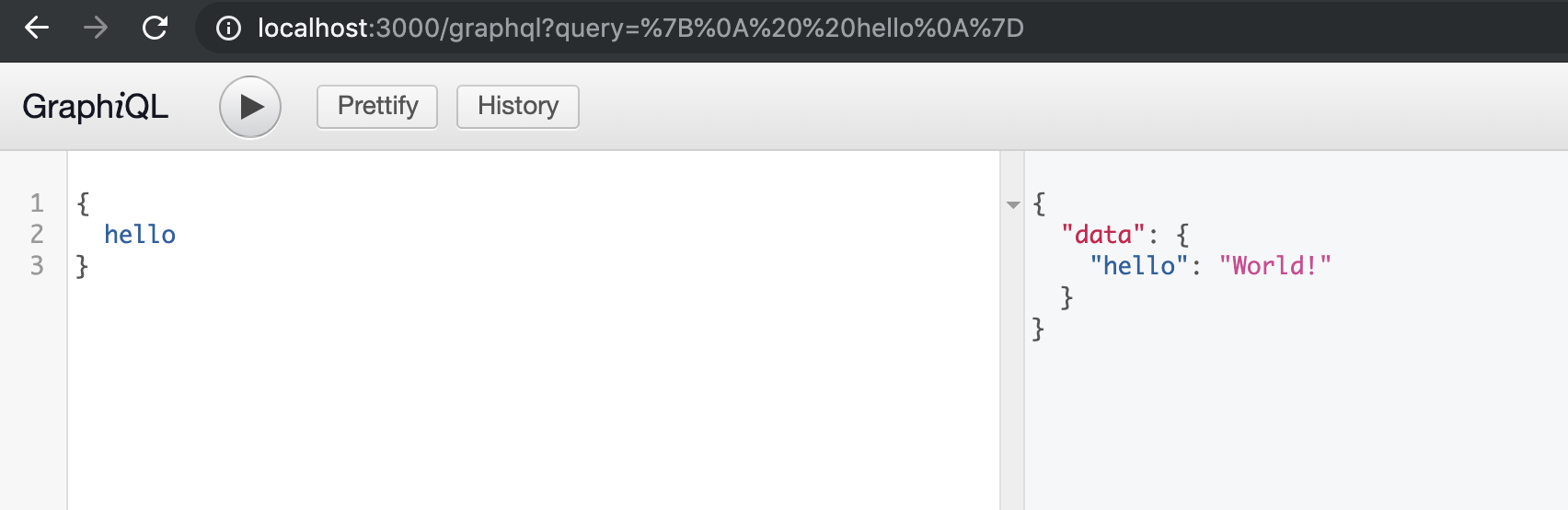
The typeDefs definition helps us construct the query.
Now, let’s use a mutation to modify the in-memory value:
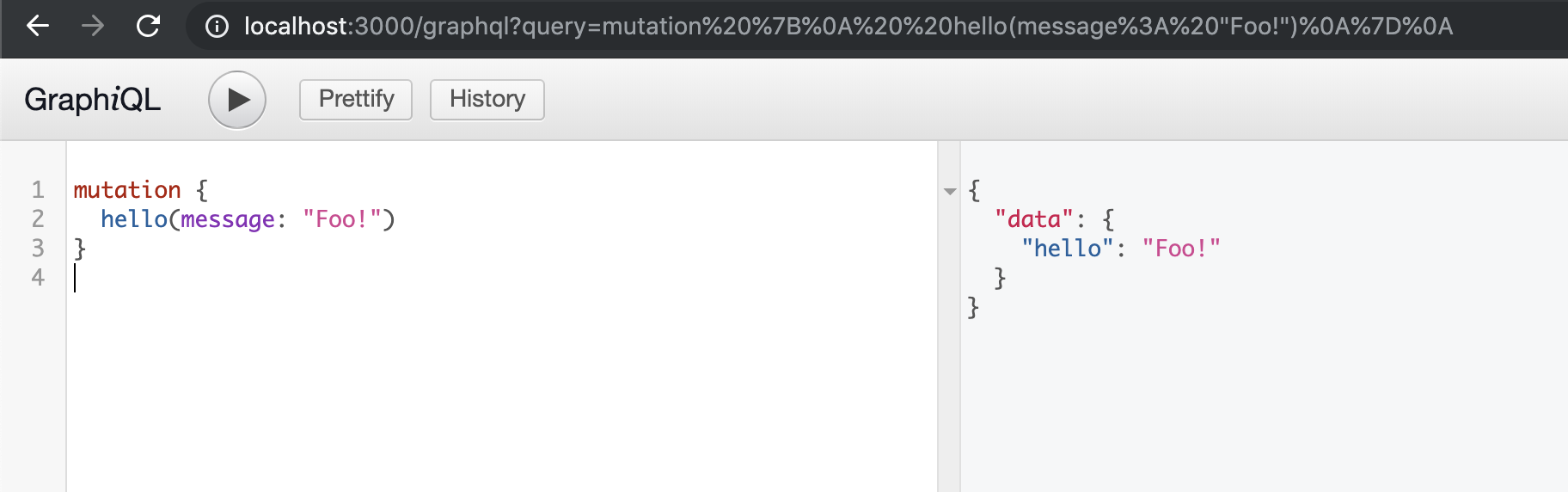
Our GraphQL Node.js API can now perform basic CRUD operations. Let’s proceed with our code.
Products
We’ll create a “products” module, using an in-memory database for simplicity. This module includes a model and a service for managing products.
Product model:
| |
Product service:
| |
Users
Following the same structure, we’ll create a “users” module with a model and service.
User model:
| |
User service:
| |
Remember, the complete source code is available link.
Now, run npm start to test our code. The server should be running on port 3000. We can access GraphQL for testing at http://localhost:3000/graphql.
Let’s add a product to our list using a mutation:
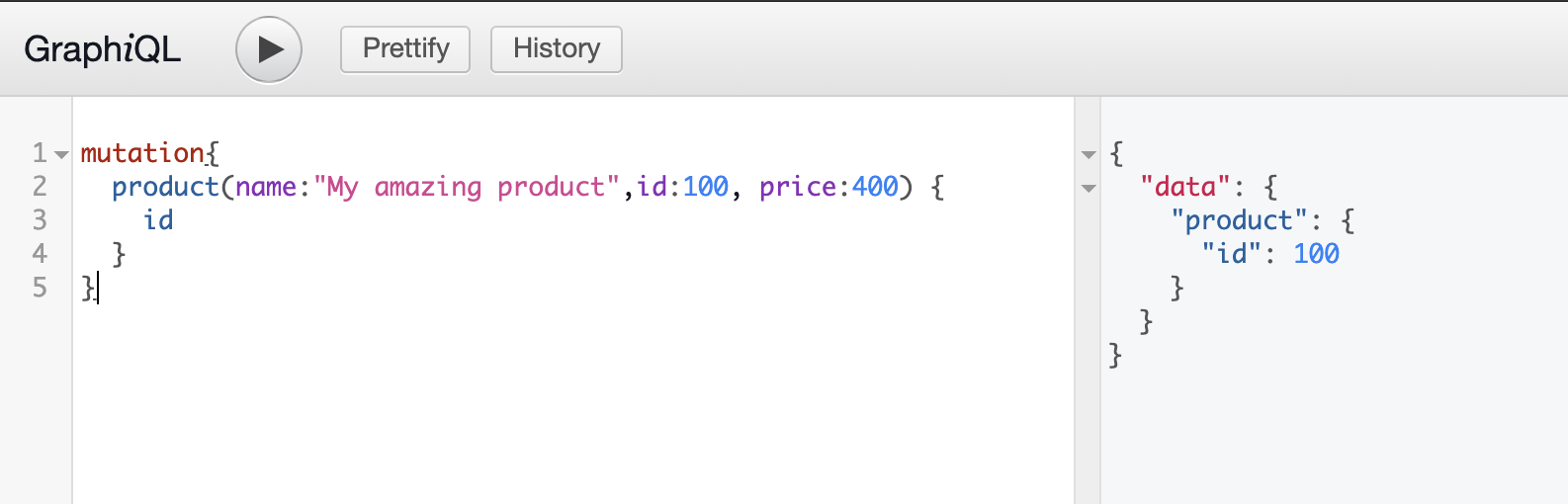
Now, let’s use a query to check if it worked, retrieving only the id, name, and price:
| |
The product is working as intended. We can now experiment with different fields. Let’s add a description:
| |
Now, let’s try working with users:
| |
And a query:
| |
The response:
| |
Our GraphQL skeleton is ready! While there’s much more to building a fully functional API, the foundation is set.
Summary and Final Thoughts
This article covered the basics of developing a GraphQL Node.js API:
- Using Node.js with Express and GraphQL.
- Basic GraphQL usage.
- Implementing queries and mutations.
- Creating modules for your project.
- Testing your GraphQL API.
For brevity, we omitted some important aspects:
- Data validation.
- Error handling.
- Field validation.
- Securing the API with JWT.
- Password hashing.
- Unit and integration testing.
The full source code is available on Git link. Feel free to use, fork, open issues, make pull requests, and experiment! Remember that these are just suggestions, and numerous approaches exist for designing GraphQL APIs. Continue exploring GraphQL to uncover its full potential and enhance your API development.