When promoting your business online, it’s crucial to ensure your pay-per-click (PPC) ads reach the right audience. Instead of targeting everyone globally, focus on specific locations where your ideal customers reside. Geotargeting, also known as local PPC, allows you to precisely target your search ads to customers in designated locations like countries, cities, or even specific neighborhoods. This strategy is incredibly beneficial for businesses that depend on local foot traffic, such as restaurants, used car dealerships, and e-commerce stores with limited delivery zones.
By implementing geotargeting, you can optimize your ad budget and avoid wasted clicks from users outside your service area. This ensures that the people who engage with your ads are more likely to convert into paying customers. geotargeting is essential if you want to make the most efficient use of your limited advertising spend.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of setting up and managing a successful geotargeted campaign, providing valuable tips and best practices to maximize your local PPC efforts.
Ready to find out what’s draining your PPC budget? Get a free Google Ads performance grade to learn where you’re struggling and how to fix it!
Setting Up Geotargeting in Google Ads
Begin by selecting the campaign you wish to target within your Google Ads account, then navigate to the Settings tab. Scroll down to the Locations and Languages section and click edit under Locations.
Targeting Locations via Search
Choose the Search tab and start entering your desired location. Select it from the drop-down menu of relevant matches. Options include country, region (like state or province), city, postal code, and even certain airports.
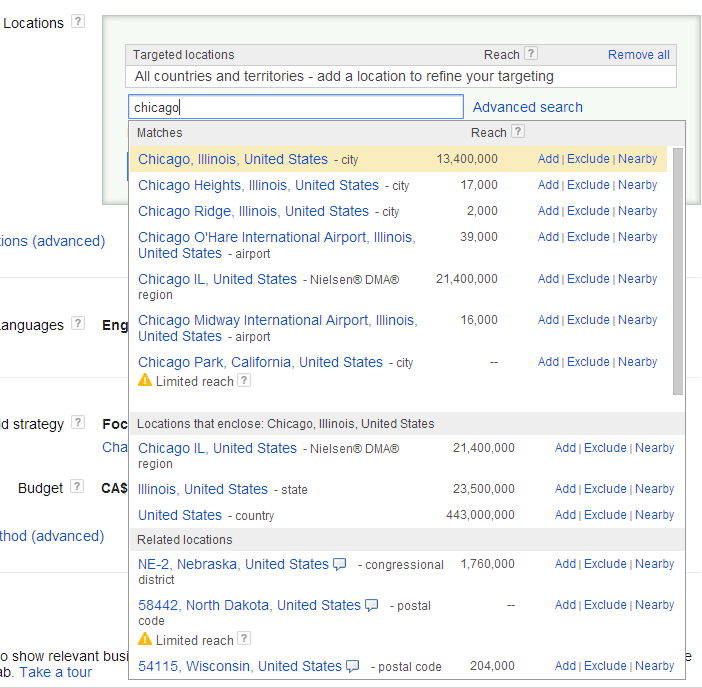
The Reach metric indicates the potential number of people who might see your ads if you choose that location. You have three options for each location:
- Add: Includes the location in your list of targeted locations.
- Exclude: Prevents your ads from being displayed in this location.
- Nearby: Generates a list of nearby regions you might want to consider adding.
As you select a region, Google Ads will show a map highlighting the targeted area.
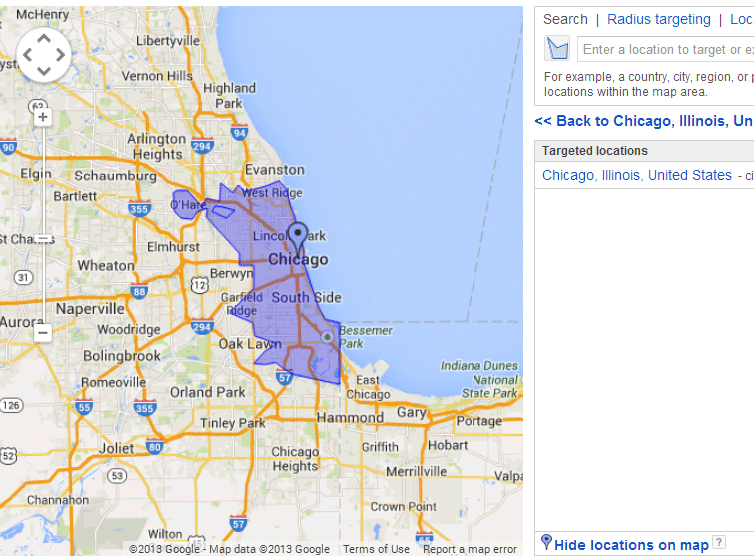
If you’ve selected multiple regions, they’ll appear in a list. To visualize all your targeted areas, go to the Selected locations tab and click Show locations for a larger map.
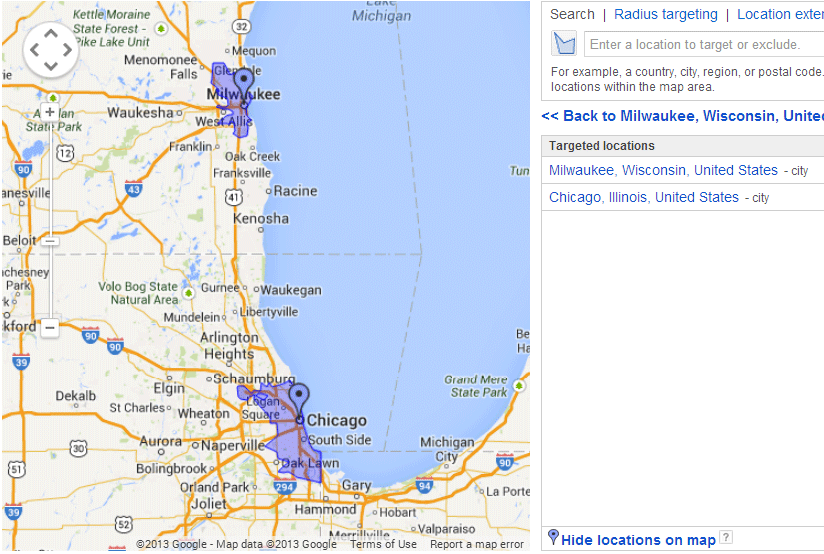
Advanced Geotargeting Options
By Radius (Proximity Targeting)
Select the Radius tab. This allows you to define a circular radius around a specific location, also called proximity targeting. Enter a location into the provided box, which will become the center of the radius. Then, specify the desired distance around that location by typing a number into the next box, choosing either miles (mi) or kilometers (km) using the drop-down menu. For instance, a restaurant could set a 10-mile radius to target customers searching within that vicinity. This strategy is particularly effective when combined with mobile-optimized ads, as local mobile searchers are often ready to make immediate purchases.
The example below demonstrates targeting a 20-mile radius around Boston.
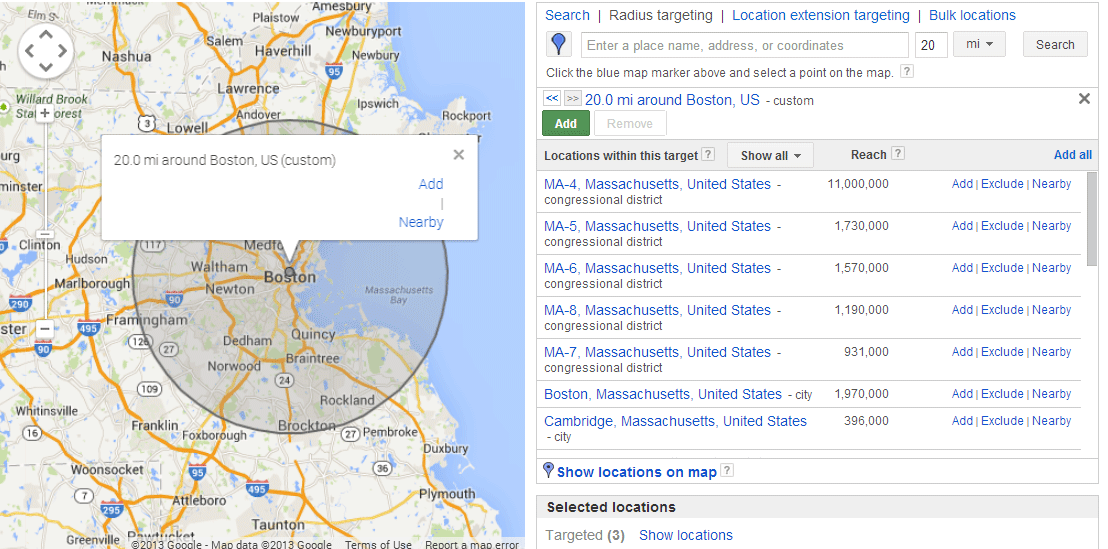
You can create a custom radius by selecting the blue map marker icon, then clicking anywhere on the map to define the radius center.
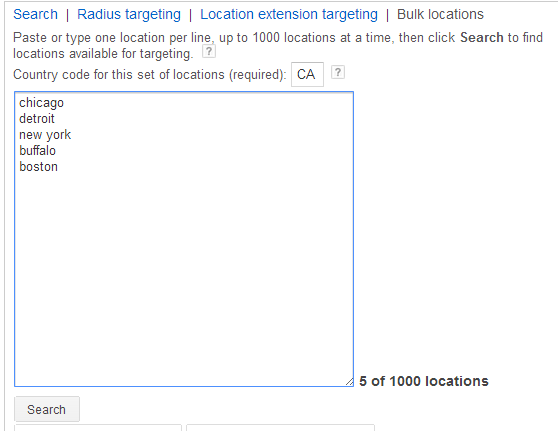
Bulk Editing Locations
The Bulk locations tab lets you efficiently add, exclude, or remove up to 1000 locations simultaneously. Simply type or paste the locations, ensuring each batch belongs to the same country. Select the country code from the drop-down menu on the right.
For your reference, here is Google’s official list of targetable locations.
Managing Your Geotargeted Campaign Effectively
To track the performance of your geotargeted campaign, go to the Settings tab and click on the Locations tab. You’ll find standard metrics such as clicks, impressions, average cost-per-click (CPC), and average position for each specified location.
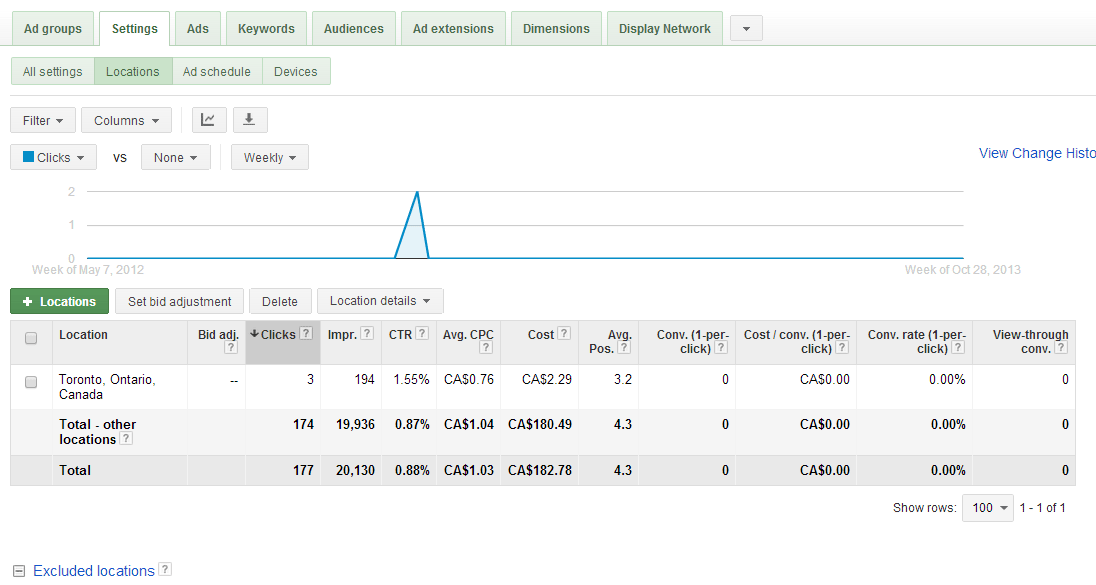
The Total – other locations row represents traffic from locations other than those you’ve explicitly targeted. While Google Ads doesn’t provide specifics about these locations, a high number suggests the need to refine your targeting by adding or excluding more locations and implementing the best practices outlined below.
To identify keywords triggering your ads outside your target locations, utilize the Search Terms Report. Go to the Campaigns tab, click Keywords, then Details, and select All to access the report. If you find irrelevant keywords, add them to your negative keyword list by checking the box next to each and selecting Add as a negative keyword. For example, a Chicago-based car dealership could add “Boston” to their negative keyword list if their ads are being triggered by searches for “new cars Boston.”
Geotargeting Tips & Best Practices for Optimal Results
Prioritize Customer Locations: Align your targeting with your business reach. If you’re an online retailer shipping nationwide, target the entire country. Conversely, a regional retail chain should target specific states and exclude others. E-commerce stores with international shipping should focus on their delivery countries using their local PPC campaigns.
Strategic Exclusions: Excluding irrelevant locations is as important as including relevant ones. For instance, if your company only ships within the mainland United States, exclude Hawaii and Alaska from your targeting.
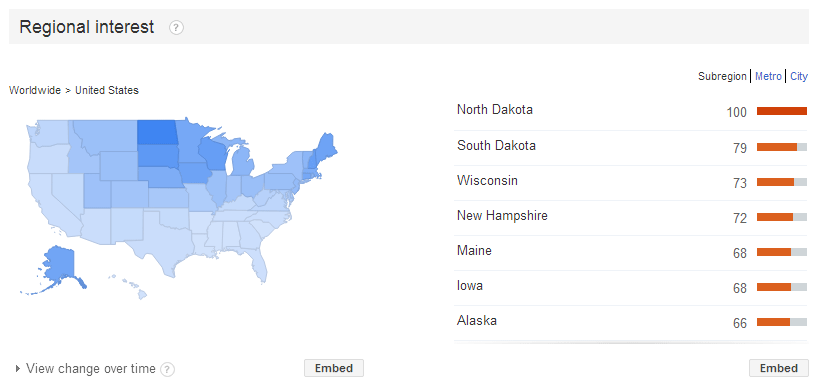
Leverage Google Trends for Regional Insights: Gain valuable insights into customer interests by using tools like Google Trends. This tool reveals search volume for specific keywords by country, subregion (state or province), metro area, or city, helping you identify regions highly interested in your offerings. The example below illustrates the top U.S. states searching for “snow blower,” predominantly those with significant snowfall.
Incorporate Regional Keywords: Include location-specific terms in your keyword lists. For instance, a Boston-based insurance company should use keywords like “boston insurance companies” and “car insurance boston.” Thanks to geotargeting, you can also incorporate broader terms like “car insurance,” as the targeting ensures these ads are shown only to local searchers. Utilize this fantastic free tool for quickly generating local keyword lists (limited to U.S. locations) to optimize your keyword strategy.
Highlight Location in Ad Text: If feasible, include your target location in the ad copy, preferably in the title. This increases visibility and relevance, as matching ad text with user search queries appears in bold.
Utilize Location and Call Extensions: Enable location extensions to display your business address and call extensions to provide your phone number in local ads. This makes it easier for potential customers to find and contact you directly.
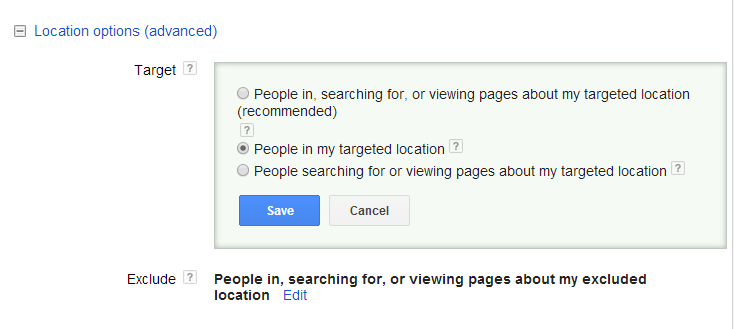
Refine Location Targeting Settings: By default, Google targets ads to people within your specified location and those searching about it. To avoid irrelevant impressions, adjust the settings in Google Ads. Go to Campaign Settings, click on Location options (advanced), and under the Target section, select “Edit” and choose “People in my targeted location.”