Before diving into this post, it’s important to know I’m someone who enjoys creating spreadsheets for online sneaker purchases and finds joy in organizing Tupperware. Basically, I love content audits! However, I recognize that not everyone shares my enthusiasm. In fact, content audits are often perceived as tedious, time-consuming, and overwhelming—which, let’s face it, they can be.
That’s why I’ve created this comprehensive guide. It’s packed with everything you need to become a content audit expert (and maybe even learn to appreciate the process). This guide covers the following:
- The definition, purposes, and benefits of content audits
- A comprehensive list of data points to collect
- Tips for conducting a successful content audit
- Six different content audit templates and examples
Quickly Access the Content Audit Templates
Important: All template links lead to the same spreadsheet! Each link corresponds to a specific tab within the spreadsheet.
- Website content audit template
- SEO content audit template
- Blog content audit template
- Landing page content audit template
- Guide content audit template
- Overall content audit template
You might also find these audits helpful:
- The 6-Step Technical SEO Audit
- The Easy, 10-Step SEO Audit
- [The 6-Part Website Audit [with an Epic Google Sheet]]
What Exactly is a Content Audit?
A content audit involves taking stock of and evaluating your business’s existing content based on specific criteria. These criteria encompass the type of content you’re auditing and the data you want to analyze.
But what kind of content might you want to audit? Content comes in various types, such as:
- Core website pages
- Landing pages
- Blog posts
- Learning center articles
- Guides
- Webinars
- Videos
- One-pagers
- Podcasts
- Success stories
- Benchmark reports
- Battle cards
- Slide decks
- Boilerplates
- Branded templates
Beyond content types, you can also consider specific content conditions:
- Content created since the beginning of time or within a defined date range.
- Auditing all your content or focusing on a particular format.
- Analyzing all content formats or narrowing it down to specific formats on a particular topic.
When it comes to data analysis, the possibilities are vast. You can explore anything you can find using Google Analytics and good old-fashioned human observation.
The key takeaway? Content audits are incredibly flexible. The scope of your audit depends on the amount of content, the tools at your disposal, and your audit’s objective—which we’ll delve into shortly.
Why Bother with Content Audits?
While content audits might seem time-consuming, they’re invaluable for creating high-quality content, strengthening your brand reputation, and enhancing your team’s overall output. Let’s explore each of these benefits in greater detail.
Content Audits as a Content Marketing Strategy Powerhouse
Regular reporting is essential for staying on track with your content marketing strategy. However, content audits offer a broader perspective, allowing you to identify areas for improvement, address specific issues, and optimize for particular goals.
The Outcome: The insights derived from a content audit can fuel SEO improvements, highlight strengths and weaknesses, uncover fresh topics, deepen your understanding of your audience, and reveal opportunities for verticalization, scaling, or repurposing your content.
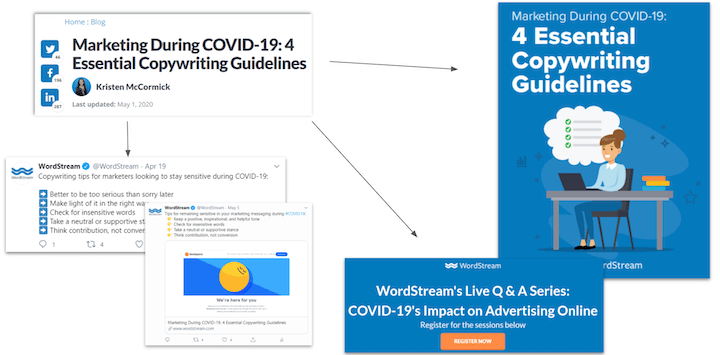
Elevate Your Brand and Reputation with Content Audits
Every piece of content you share with your audience speaks volumes about your brand. You definitely don’t want to project an image of being outdated, careless, or incompetent. Your industry, offerings, and brand are constantly evolving, and it’s crucial to stay ahead of the curve.
The Outcome: Content audits are your secret weapon for maintaining consistency in design and tone, ensuring information accuracy, and cultivating a polished online presence. You can even incorporate competitor analysis to stay abreast of industry trends.
Regular content audits act as guardians of your brand’s reputation, making sure that every interaction with your content is a positive one, radiating authenticity, expertise, and trustworthiness.
Content Audits: Boosting Organizational Output
Comprehensive content audits are the architects of a thriving content library for your business. A shared content library is a treasure trove of valuable assets.
The Outcome: When other departments can readily access and leverage the content team’s creations, it paves the way for effortless content recycling and repurposing—saving time and elevating the quality of their materials (think one-pagers, slide decks, sales enablement resources).
Furthermore, if the content team has visibility into content generated by sales, product marketing, branding, and PR (both internal and external), they gain insights into key themes, important topics, and valuable context for departmental requests.
An often-overlooked operational advantage of a content library is its ability to onboard new team members seamlessly, regardless of whether they’re managing or utilizing the content.
What Should Your Content Audit Encompass?
Content audits can serve a multitude of purposes, so there’s no one-size-fits-all checklist of data points. However, below is a comprehensive list of information to consider including in your content audit.
Keep in mind that this list is not exhaustive, and some data points overlap. Additionally, some items can serve as action items in themselves. Remember, you don’t need to collect every single data point! Think of this list as a menu—select the items that align with your specific goals.
Informational Content Audit Checklist
Informational data provides objective facts about the content being audited. While some information needs to be gathered manually, website plugins and tools can automate data extraction.
Summaries: Provide concise overviews of the content pieces. This might be redundant if you’re already including meta descriptions (or if not, use these summaries as your meta descriptions).
Titles: Page titles and SERP titles can differ. Ensure consistency for a seamless user experience, with anchor text and CTA buttons aligned with the page title.
Meta Title/Title Tags: This is the title displayed on the SERP, and analyzing it alongside click-through rates (CTR) can be insightful.
Meta Descriptions: These concise descriptions appear on the SERP. Incorporate them into SEO audits to optimize keyword usage and ensure adherence to Google’s character count limits.

Date Published: Even with the publish date in the URL, including it here provides context for traffic data and enables date-based organization. A post at the bottom of a top ten list might be performing exceptionally well considering its recent publication date.
Date Last Modified: This is particularly relevant for guides or static content. It helps identify guides published before or after significant changes (e.g., branding updates, changes in guide offers, or even Google’s name change from AdWords to Google Ads).
For frequently updated blog posts, this might be less crucial. However, a focused SEO content audit on select posts should definitely include modification dates and specific changes made.
Product or Service Supported: This might be embedded in categories and tags for blog posts and can be extracted using website export tools. This information is invaluable for building a library for other departments to source sales enablement materials, newsletter content, and landing page copy. It also highlights products or services needing more content support.
URL: This is the publicly accessible link to your content (blog post, YouTube video, etc.).
Location: This refers to the media file’s location on your server.
Keywords: Include targeted keywords along with their volume and difficulty scores. This allows for prioritization based on impact and effort when seeking optimization opportunities. For example, it might not be worthwhile to invest time in optimizing for a low-volume keyword. Conversely, if a post targeting a high-volume keyword isn’t performing well, consider retargeting it for a less competitive variation. It’s often more beneficial to rank on page one for a keyword with 500 searches than on page five for one with 2,300.
Word Count: Identify short posts that could be consolidated into more substantial, higher-ranking content. It’s also helpful for analyzing metrics like time on page. If a 2,500-word post has an average time on page of 10 seconds, something needs attention.
Shares: Don’t manually collect social media insights. Include this data point if your blog posts have share counters.

Qualitative Content Audit Checklist
Qualitative data requires manual gathering, which can be time-consuming. However, it’s essential for upholding content quality, brand consistency, and reputation in a constantly evolving digital landscape.
Images: Evaluate the presence, quality, and relevance of images. Check for outdated screenshots and ensure accuracy.
Broken Images or Links: These negatively impact user experience and SEO, so identify and fix them.
Tone: Does it resonate with your brand voice?
Language: Update terminology to reflect branding changes, retired products or services, or industry shifts.
Forms: Test landing page forms to ensure a smooth user experience. Verify that information flows correctly into your CRM and other automation platforms.
Comments: Use a comment moderation tool or manually review comments. Ensure timely responses to comments (positive and negative) and remove spammy comments that could result in Google penalties for unnatural external links. Comments can also spark unique blog post ideas.
Offers: Review pop-ups, bottom rails, and side rail offers for freshness. Ensure they’re not appearing in unintended locations.
Readability: While readability tools are helpful, nothing replaces human judgment. Scroll through the content to ensure it’s engaging, easy to read, and skimmable.
Spelling/Grammar/Compliance with Style Guide: Not all content originates from the content team! This is crucial for maintaining consistency in product descriptions, pitch decks, one-pagers, and more.
Accuracy/Freshness: Is the information current? Can stats be updated? Are listed tools still relevant? Consider adding recent links to enhance the content’s value.
Competitor Equivalent: Provide links to similar content from competitors or other brands for inspiration.
Ideas to Improve: Include an open-ended section for auditors to share additional notes or ideas that might fall outside the specific audit’s scope.
Quantitative Content Audit Data Points
Numbers provide an objective basis for setting measurable goals and tracking them with content marketing KPIs. They’re also vital when auditing site health and performance.
Depending on what you’re measuring and the volume of content, you can obtain some information from Google Analytics and Google Search Console. For more in-depth data, consider using audit tools like ahrefs or Screaming Frog.
Explore our SEO metrics post for more information on these data points.
Organic Pageviews: The number of users accessing a page from search engine results.
Bounce Rate: The percentage of visitors who leave without exploring additional pages.
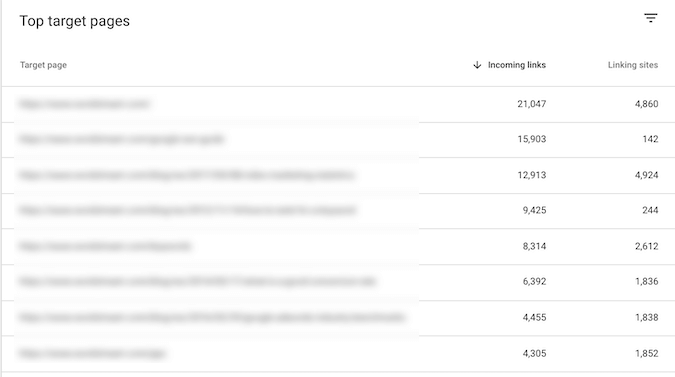
Internal Links: Track the number of internal links, checking for broken links or opportunities to link to newer, more relevant content.
Incoming Links: Monitor the number of backlinks. An excessive number could indicate unnatural link building practices, potentially leading to Google penalties.
Linking Sites: A single website might link to your page multiple times, so this number is typically lower than the total backlink count.
Keyword Volume/Keyword Difficulty: Refer to the informational data section!
Page Load Speed: While related to technical SEO, content-level adjustments can improve this metric. For a small number of pages, use the free Page Speed Insights tool. For larger audits, use an audit or SEO tool.
Average Position: Manually obtainable from Search Console, but an audit or SEO tool simplifies the process. It’s especially helpful for identifying pages that are on the cusp of page one, presenting optimization opportunities.
Time on Page: This metric helps identify if something on your page is amiss, whether it’s unengaging content or a mismatch between content and keyword intent.
Conversions: More relevant for landing page content audits, as Google Analytics defines conversions broadly. However, it’s useful if you have goals configured in Google Analytics.
Conversion Rate: Essential for understanding top-performing content. User experience (UX) significantly impacts conversion rate.
Bounce Rate: Useful for various content audits, but a high bounce rate isn’t always bad. A blog post with a reasonable time on page and high bounce rate might indicate that it’s effectively providing the information searchers seek.
Exit Rate: Shows how frequently a specific page was the last one visited in a session.
Image Size: Consider both the image dimensions and the file size.
Sales metrics like CPA, leads generated, leads nurtured, closes, and ROI are important but fall outside the scope of content audits discussed here.
How to Conduct a Content Audit (and Actually Succeed)
While there’s no rigid set of rules, here are some pointers for a successful content audit:
1. Define a Crystal-Clear Goal
Content audits can easily become overwhelming. The possibilities and metrics to gather are endless, and you’ll inevitably uncover additional ones along the way. Having a clear goal helps you focus on collecting only the most relevant data. Too much information makes it challenging to extract meaningful insights.
This focus also helps you differentiate between essential changes and nice-to-haves (or ideas to revisit later) when incorporating open-ended qualitative data points.
2. Stay Organized—Your Sanity Depends on It
Spreadsheets are your best friend. Here’s how to maintain order:
Minimize open-ended cells, especially for large audits. This makes it easier to organize and sort data later.
Consider drop-down menus with predefined options, especially with multiple auditors working on the same sheet.
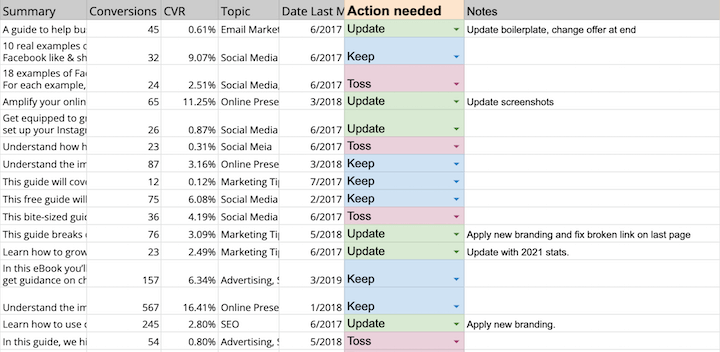
Color-coding can be a lifesaver when dealing with various content types and formats.
Specify date ranges for quantitative metrics.
Use tabs to organize extensive audits by content format, merging them later if needed. Ensure consistent column formats across all sheets.
Dedicate the first tab to instructions or checklists.
3. Choose Your Format Wisely
Content audit formats can vary:
Inventory as Action Items: In some audits, the data points themselves serve as action items. Completing the audit inherently addresses the goal. This format works well for basic QA audits involving minor but important changes that don’t require extensive tracking. The first tab might contain the action item checklist, while the second tab has columns for title, link, and status.
Inventory for Action Item Identification: Other audits involve collecting data first and then collaborating to determine action items based on the goal.
Hybrid Approach: Many audits use a combination of both approaches.
Regardless of how and when action items are identified, ensure they’re specific and assigned to a clear owner.
4. Embrace Content Audit Tools
Several tools can streamline your content auditing process:
Google Tools: Analytics, Search Console, Page Speed Insights.
SEO and Spider Tools: semrush, ahrefs, Screaming Frog.
Inventory Organization Tools: Airtable, Google Sheets.
Content Quality Tools: Yoast SEO Plugin, Grammarly, Hemingway editor, and a reliable bulk web page word count checker.
Image Extractors: Tools like extract.pics.
ROI Tools: Your CRM can provide valuable insights.
Website Graders: These tools offer comprehensive assessments, covering everything from accessibility to SEO.
5. Auditing and Reporting: Two Sides of the Same Coin
Content audits should complement, not replace, regular reporting. Audits are typically more comprehensive and conducted quarterly or annually (except when troubleshooting specific issues).
Regular reporting is essential for tracking KPI progress and identifying long-term patterns. A deep understanding of your metrics and content types simplifies criteria selection for future audits.
How to Run a Website Content Audit
Here, a website content audit refers to an audit that covers the core pages of your website. It’s a fundamental aspect of website maintenance. You can also include a representative example from a templated page type, such as a blog post or landing page.
Example Pages to Audit:
- Homepage
- About
- Contact
- Products/services
- Pricing
- Success stories/testimonials
- Gallery/portfolio
- Resources
- Careers
- Leadership
- Meet the team
- Events
- FAQ page
- Blog homepage
- Typical blog post page
- Email signup landing page
- Content download landing page
- Content download thank you page
- Press
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & conditions
- Search results
- Navigation menu
Example Website Content Audit Goals:
- QA after a site migration or rebrand.
- Update product terminology.
- Boost engagement and conversions.
- Ensure inclusivity.
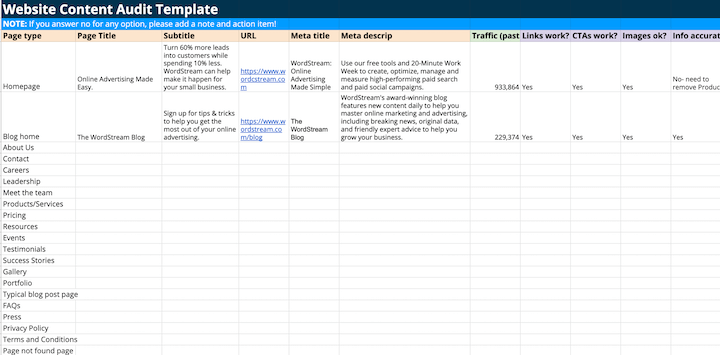
Example Website Content Checklist:
- Page title
- Page subtitle
- URL
- Meta title
- Meta description
- Traffic
- Link functionality
- CTA functionality
- Image quality and relevance
- Information accuracy
- Spelling and grammar
- Pop-up presence
- Bounce rate
- Notes
Example Website Content Audit Insights and Action Items:
- The leadership page needs updating with new headshots and bios.
- The resources page has a high bounce rate; simplify with menus and add thumbnails for featured resources.
- The “About Us” page lacks personality. Move that content to the “Contact” page and rewrite it with brand voice and history.
- The success stories page has low traffic; add it to the main navigation menu.
Website Content Audit Template
Use this template: Make a copy of this Google Sheet. Feel free to tailor it to your needs by adding, editing, or removing data points—and then, get to work!
Click to open this free website content audit template
How to Run an SEO Content Audit
An SEO content audit focuses on website pages indexed by Google. Tools like Ahrefs or Screaming Frog are invaluable for this process.
Example SEO Content Audit Goals:
- Increase website traffic.
- Improve the ranking of SEO content.
- Uncover new keyword opportunities.
- Enhance Core Web Vitals.
- Remove or optimize underperforming content.
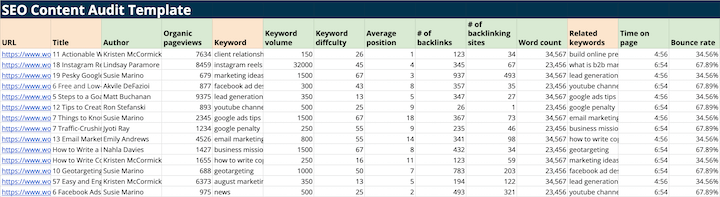
Example SEO Content Audit Checklist:
- URL
- Title
- Meta title
- Meta title character count
- Meta description
- Organic pageviews
- Keyword (with volume and difficulty)
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Average position
- Word count
- Internal links
- Page load time
- Number of images
Example SEO Content Audit Insights and Action Items:
- Several blog posts are ranking on page two of search results; optimize them to reach page one.
- The overall PageSpeed Insights score is low; compress and resize images on the top 30 most trafficked pages.
- Blog posts with fewer than 500 words have low organic traffic; consolidate and redirect them to a single, comprehensive long-form post.
Are you making SEO mistakes? Get a free SEO audit with the LOCALiQ website grader and find out!
SEO Content Audit Template
Use this template: Make a copy of this Google sheet. Add, edit, and remove data points as needed to make it your own—and dive into optimizing your SEO content!
Click to open this free website content audit template
How to Run a Blog Content Audit
While a blog content audit can overlap significantly with an SEO audit, not all blog posts are created for SEO. Blogs serve purposes beyond simply driving traffic to your website.
Example Blog Content Audit Goals:
- Identify key topics to focus on.
- Strengthen brand messaging.
- Increase reader engagement.
- Improve conversion rates.
- Enhance accessibility and inclusivity.
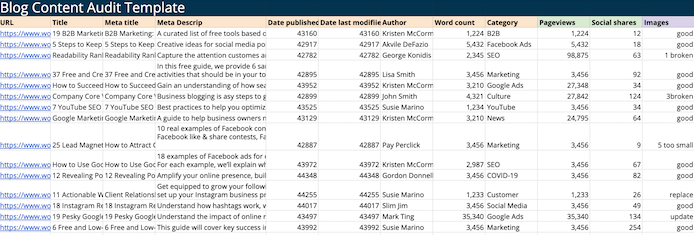
Example Blog Content Audit Checklist:
- URL
- Organic pageviews
- Title
- Meta title
- Meta title character count
- Meta description
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Category
- Product supported
- Image quality, inclusivity, branding (e.g., updated logo)
- Image alt text (keyword-rich and accessible?)
- Comments
- Brand alignment
- Style guide compliance
- Top search queries
- Target keyword (with volume and difficulty)
- Word count
- Information accuracy
- Number of internal links
- Social shares
- Pop-up effectiveness
Example Blog Content Audit Insights and Action Items:
- Post X has several comments about Y—address them in the post.
- LinkedIn shares are nonexistent for all posts—troubleshoot and fix.
- Content in category X/supporting product Y is lacking—conduct keyword research and publish three targeted posts by the end of the quarter.
- Repurpose posts X, Y, and Z into webinars next quarter. Combine posts A and B into a downloadable PDF guide.
- Identify posts targeting highly competitive keywords and adjust them to focus on less competitive, long-tail keywords with lower volume but higher intent.
- Update the pop-up for category X to improve its conversion rate.
Blog Content Audit Template
Ready to supercharge your blog content? Use this template: Make a copy of this Google Sheet. Customize it to your liking by adding, editing, or removing data points—and let’s get this audit rolling!
Click to open this free blog content audit template
How to Run a Guide (or Ebook or White Paper) Content Audit
Consider auditing landing pages for paid guide promotions separately.
Example Guide Content Audit Goals:
- Increase resource page conversion rates.
- Prioritize rebranding efforts.
- Identify guides for pop-up or ad promotions.
- Streamline the content library.
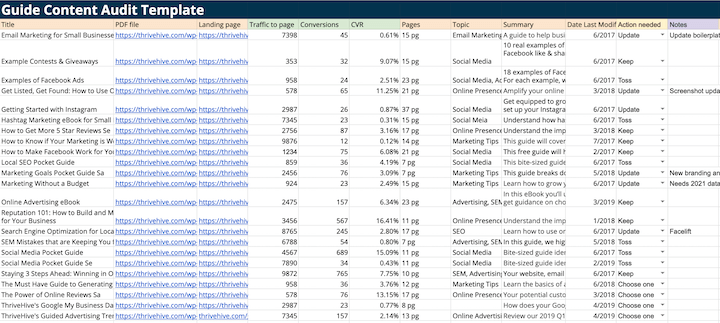
Example Guide Content Audit Checklist:
- Guide name
- Creation date
- Last modified date
- PDF link
- Landing page link
- Landing page traffic
- Landing page conversion rate
- Referring link
- Word count
- Page count
- Stage of the funnel
- Industry vertical
- Boilerplate usage
- Offer at the end
- Template used
Example Guide Content Audit Insights and Action Items:
- Retain guides A-L, update guides M-T, and remove guides U-Z.
- Consolidate guides A, B, and C into a comprehensive toolkit.
- Incorporate guides X, Y, and Z into nurture email sequences.
Guide Content Audit Template
Time to optimize those valuable guides! Use this template: Make a copy of this Google sheet,. Feel free to adapt it by adding, editing, or removing data points—and let’s get those guides in top shape.
Click to open this free guide content audit template
How to Run a Landing Page Content Audit
Auditing all existing landing pages might not be feasible, especially for businesses with numerous pages or complex URL structures. It’s also unnecessary for non-indexed landing pages that don’t impact SEO.
Example Landing Page Content Audit Goals:
- Drive more traffic to landing pages.
- Increase conversion rates.
- Test form functionality and CRM integration.
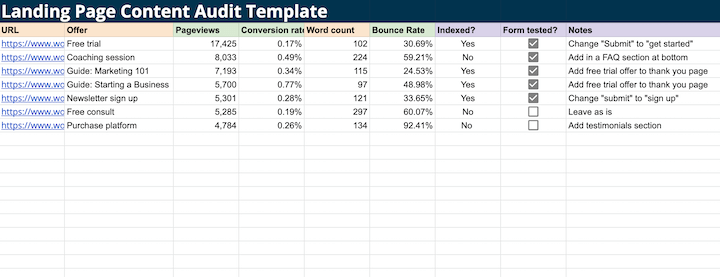
Example Landing Page Content Audit Checklist:
- Title
- Indexed status
- Meta title
- Meta description
- Offer clarity
- Pageviews
- Sessions by source
- Conversions/conversion rate (CVR)
- Average time on page
- Bounce rate
- Word count
- Areas for improvement (clear value proposition, personalization, social proof, form optimization, CTA effectiveness, missing information)
- Form functionality
- Content delivery confirmation
- Lead routing verification
- Thank you page effectiveness
- Ideas for improvement
Example Landing Page Content Audit Insights and Action Items:
- Landing pages with higher word counts have higher conversion rates—increase word count on pages X, Y, and Z.
- Pages A, B, and C have high bounce rates—investigate and optimize.
- Disable live chat on a specific landing page.
- Noindex landing pages X, Y, and Z.
- Troubleshoot and fix the broken form on page Z.
- The homepage drives the most traffic to landing page X, but landing page Y converts significantly better—test using page Y’s format for page X.
- Explore opportunities for adding CTAs to thank you pages.
Landing Page Content Audit Template
Turn those landing pages into conversion machines! Use this template: Make a copy of this Google sheet. Make it your own by adding, editing, or removing data points—and let’s optimize those landing pages for success.
Click to open this free landing page content audit template
How to Run an Overall Content Audit
This comprehensive audit encompasses all forms of media your business produces:
- Guides
- Infographics
- White papers
- Webinars
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Blog posts (consider focusing on top performers if you have a large volume)
It also includes all content types:
- Educational content
- Case studies/success stories
- Benchmark reports
- Product tutorials
- One-pagers
- Pitch decks
Example Overall Content Audit Goals:
- Create or audit a centralized content library for all departments to access and reuse.
- Update or remove outdated content.
- Provide a new manager with a comprehensive overview of existing content strategy and output.
- Identify content repurposing opportunities.
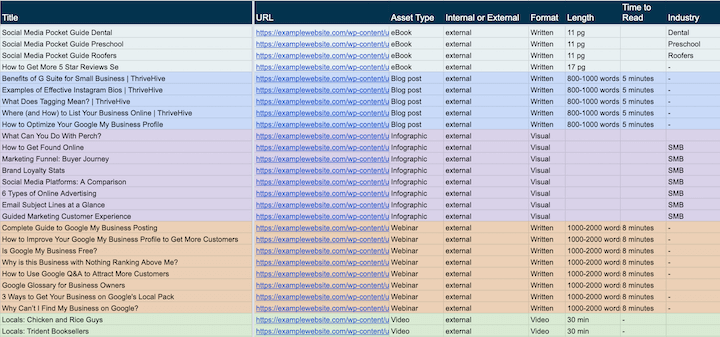
Example Overall Content Audit Checklist:
- Content name
- Title
- Content type
- Content format
- Length (word count, page count, reading time)
- Date last modified
- Stage of the funnel
- Product supported
- Internal or external use
- Industry vertical
- Traffic to page
Example Overall Content Audit Insights and Action Items:
Since the goal of an overall media audit is to create or update a comprehensive content library, the primary action item is to complete the inventory. While collecting information, make minor on-the-go improvements and fixes (where time-efficient). More involved optimizations and action items can be tackled through format-specific audits.
Overall Content Audit Template
Ready to wrangle all your content assets? Use this template: Make a copy of this Google sheet. Customize the data points as needed—and let’s get this comprehensive audit underway!
Click to open this free overall content audit template
Kickstart Your Content Audit with These Tips and Templates
As we’ve explored, content audits are vital for achieving traffic, engagement, conversion rate, and ROI goals. They ensure consistent high-quality content creation, maximize content impact, and strengthen your brand’s reputation.
This guide’s data points and templates provide a roadmap to initiate and successfully execute any content audit you need.
And just in case you haven’t had enough lists, here’s a final one with links to all the spreadsheets:
Remember: Each template link directs you to the same spreadsheet, but to a specific tab within it. Website content audit
- SEO content audit
- Blog content audit
- Guide content audit
- Landing page content audit
- Overall content audit
Hungry for More Templates?
Check out these 62 Free Marketing Templates You Didn’t Know You Needed. You’re welcome!