As a digital marketer, I often encounter clients struggling to understand duplicate content—what it is, how to prevent it, and why it’s important.
This article debunks common myths about duplicate content and SEO in a post-Panda world, and provides tips for staying on Google’s good side, ensuring both search engines and users love your content.
Understanding Duplicate Content
A Google Search Console Help Centre article defines duplicate content as: “_…_substantive blocks of content within or across domains that either completely match other content or are appreciably similar.”
While this seems straightforward, the question is: how does this impact your website?
Here are some instances of duplicate content:
Ecommerce Product Descriptions: This refers to using generic descriptions from suppliers across multiple sales platforms. For instance, the Nespresso website’s description of a coffee machine…
…is copied verbatim on Amazon India for the same product:
Reusing Pages: Common in ecommerce, this involves using the same page in different sections of your site, like: myfictionalshop.com/jackets/red-jacket.html mirroring myfictionalshop.com/sale/red-jacket.html
Similar Service Pages: Having multiple service pages on your website that are too alike.
WWW and Non-WWW Issues: Your site doesn’t effectively manage both www and non-www versions.
Using External Content: This includes using content from other websites, such as press releases published on multiple platforms, or websites that syndicate content without originality.
Multiple Domains, Similar Products: Owning several domains that target different audiences (e.g., consumers and trade) with similar product lines.
Why Worry About Duplicate Content?
Let’s debunk a major myth: Google does NOT penalize for duplicate content.
This was clarified in a Google Q&A last June. You can watch the entire video here.
However: Google might exclude some content from search results if your site has duplicate content issues. As always, Google prioritizes showing the most relevant content to users.
While Google indexes these pages, if it identifies the same content across multiple pages, it will only display the one deemed most relevant to the user’s query.
There’s a difference between CMS-generated duplicate content with new URLs and large-scale content replication for profit or ranking manipulation.
Google’s quality guidelines are clear: using illicit content generation tactics or creating pages without original content risks removal from search engine results pages (SERPs).
In typical cases like those listed above, the worst outcome is your site not appearing in SERPs.
Detecting Duplicate Content
Several tools can help pinpoint areas for improvement on your website:
Moz’s paid crawler tool (with a 30-day free trial) identifies duplicate pages and their counterparts.
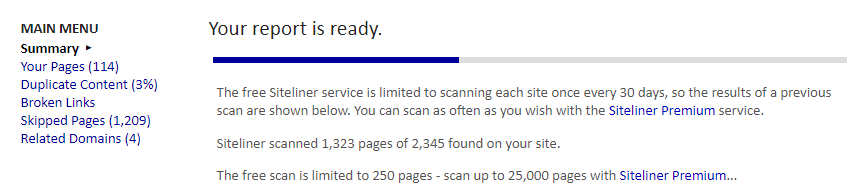
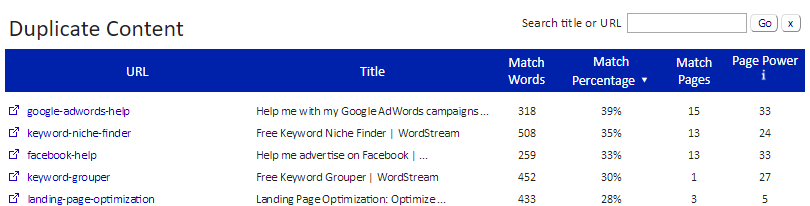
Siteliner provides a deeper analysis of duplicated pages, their similarity, and the replicated text portions. This is helpful when large text blocks are reused without being complete duplicates:
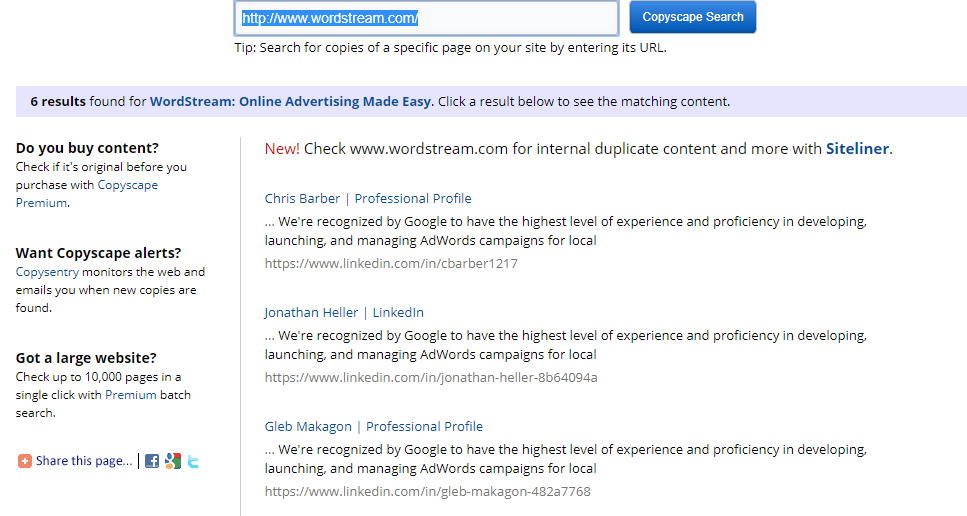
Copyscape’s plagiarism checker identifies copies of your pages on the web:
If these tools are inaccessible, search for snippets of text from your site to see if direct duplicates appear in the results.
Resolving Content Duplication
The solution depends on the duplication type. Some techniques require SEO expertise, potentially needing an agency’s assistance.
Problem: Generic Product Descriptions
Solution: Simple but potentially demanding—make your content unique, valuable, and engaging. Manufacturer descriptions explain the product; you need to convey why your customer needs it and should buy from you.
Use product specifications as a foundation and build upon them with your brand voice and personality. Consider your target audience and their needs. Explain how your product solves their problems and highlight your unique selling proposition.
Problem: Same Page in Multiple Locations
Solution: Use a canonical URL on duplicate pages, pointing to the original as the preferred version. For example, if a red jacket appears in both “sale” and “jackets” categories, the duplicate page should have a canonical tag like this:
Problem: Similar Service Pages
Solution: Enhance page distinctiveness. However, if topics overlap significantly, consolidate them into one comprehensive page. Remove the less valuable page and apply a 301 redirect to the more valuable one. One strong page outperforms two weak or conflicting ones.
Problem: WWW and Non-WWW Issues
Solution: Test by removing “www” from a URL in your browser. Ideally, a redirect should occur.
Note: Consistency is key. Choose one format (www or non-www) and stick with it. Specify your preferred version in Google Search Console.
Problem: Openly Using External Content
Solution: Common with press releases or feeds used to populate site sections (e.g., displaying regional events).
There’s no strict rule. If this content benefits users, accept potentially lower rankings for those pages, or invest in customizing it for your audience.
Problem: Separate Websites, Same Products, Different Audiences
Solution: Complex. From a search perspective, consolidating into one website is best. Business reasons might justify separate brands for different audiences. However, acknowledge their competition within SERPs.
In Conclusion…
Adhering to Google’s quality guidelines is crucial. Create valuable, trustworthy, engaging, and, ideally, unique content.
Google effectively detects unintentional duplication. These tips help search engines and users understand your site.