Retargeting, also known as remarketing, is a fundamental aspect of PPC advertising. It involves targeting ads to specific groups based on their past actions or behaviors. The effectiveness of this strategy is undeniable.
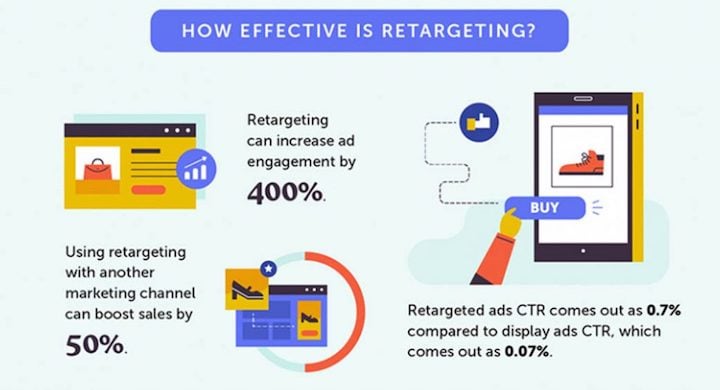 Image source
When executed properly, retargeting has the potential to boost ad engagement by an impressive 400% and increase sales by 50%. This article will guide you on how to optimize your retargeting campaigns by highlighting ten common pitfalls to avoid.
Image source
When executed properly, retargeting has the potential to boost ad engagement by an impressive 400% and increase sales by 50%. This article will guide you on how to optimize your retargeting campaigns by highlighting ten common pitfalls to avoid.
10 Common Retargeting Mistakes to Steer Clear Of
The landscape of PPC advertising is constantly changing, making it crucial to stay updated and adapt your strategies accordingly. To ensure your retargeting campaigns are as impactful as possible, it’s essential to avoid these common mistakes.
1. Relying on Cookie-Based (Website Visitor) Retargeting
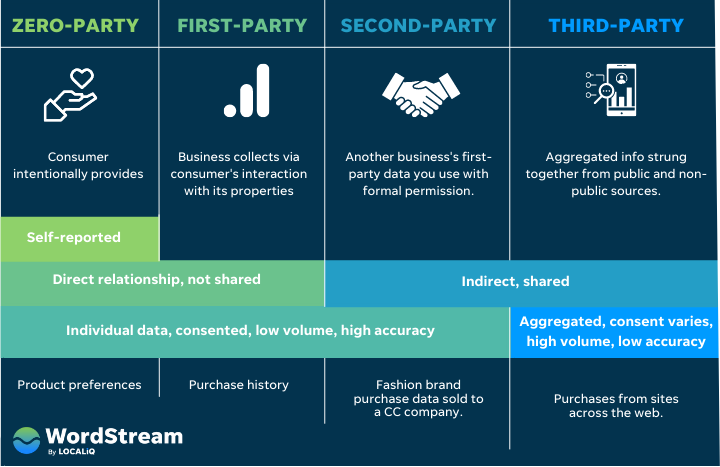
While targeting ads based on website visits has been a standard practice, the phasing out of third-party cookies poses a challenge. This shift can lead to incomplete data about website visitors, potentially resulting in mismatched messaging. Instead of relying on third-party cookies, prioritize the use of customer lists and other first-party data sources. First-party data refers to information obtained directly from users with their consent, encompassing contact details, on-page behavior, and other data points. It’s crucial to remember that purchasing contact lists does not qualify as first-party data and should not be utilized for retargeting, as it can lead to ad account suspension. The majority of ad platforms, including Google, Facebook, Microsoft, LinkedIn, Twitter, and others, enable advertisers to target ads based on uploaded or synchronized lists of customer emails and phone numbers. This approach, known as remarketing (both for targeting and excluding), leverages first-party data to ensure messages resonate with the intended audience.
 These lists can be utilized to create remarketing audiences or as a foundation for Similar/Lookalike Audiences.
It’s crucial to establish a strategy that fosters trust with customers, encouraging them to provide their contact information, for instance, by offering valuable lead magnets.
These lists can be utilized to create remarketing audiences or as a foundation for Similar/Lookalike Audiences.
It’s crucial to establish a strategy that fosters trust with customers, encouraging them to provide their contact information, for instance, by offering valuable lead magnets.
2. Avoiding Lookalike Audiences for Greater Control
Similar Audiences (Google Ads) and Lookalike Audiences (Facebook Ads) are invaluable tools for prospecting. These audiences are generated by identifying individuals exhibiting desirable characteristics and then using them as a model to discover new prospects. Initially, there were concerns about the potential for wasted ad spend with Similar Audiences, as advertisers often prefer more control over their campaigns. However, Similar and Lookalike Audiences frequently outperform direct remarketing campaigns and are significantly more effective than not using any audience targeting at all. It’s important to note that the effectiveness of Similar and Lookalike Audiences depends on the quality of the seed lists used to create them. Similar Audiences are generated automatically, whereas Lookalike Audiences need to be created manually within the respective ad platform’s interface.
 Important: Ad networks allow you to define the desired level of similarity between users and the seed audience. It’s recommended to opt for a 1% similarity setting, as higher percentages tend to result in a less-targeted audience.
Important: Ad networks allow you to define the desired level of similarity between users and the seed audience. It’s recommended to opt for a 1% similarity setting, as higher percentages tend to result in a less-targeted audience.
3. Underutilizing Audience Exclusions
Excluding specific audiences is an often overlooked but highly effective tactic for optimizing ad spend and improving targeting precision. Similar to negative keywords and placement exclusions, audience exclusions prevent individuals within the excluded group from seeing your ads. Excluding remarketing lists used as seeds for Similar Audiences ensures that your ads are shown only to new prospects. Additionally, you can exclude audiences that are closely related but not directly relevant to your target market. For instance, in real estate marketing, searches for commercial and residential properties might overlap even though their value propositions differ significantly. By excluding the in-market audience for the irrelevant sub-sector, advertisers can safeguard their budget and maintain a high-quality lead flow.
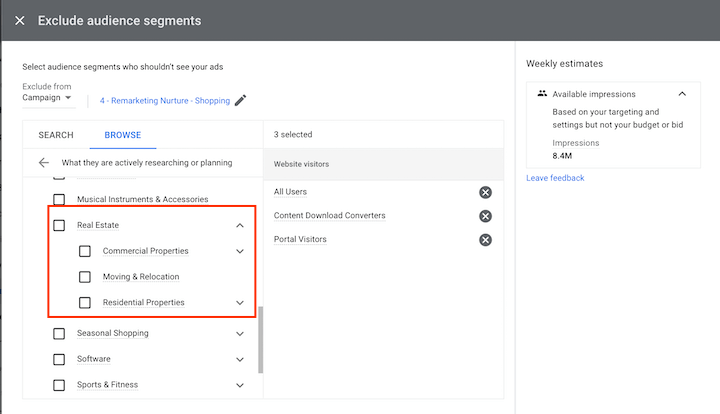 Important: When using automated bidding strategies or Smart Bidding, excluding or explicitly targeting audiences is crucial for guiding the ad platform’s budget allocation. With manual bidding or enhanced CPC, positive and negative bid adjustments can be employed to prioritize or de-emphasize specific audiences.
Important: When using automated bidding strategies or Smart Bidding, excluding or explicitly targeting audiences is crucial for guiding the ad platform’s budget allocation. With manual bidding or enhanced CPC, positive and negative bid adjustments can be employed to prioritize or de-emphasize specific audiences.
4. Neglecting SEO Insights
Integrating Google Analytics with your ad account unlocks valuable audience syncing capabilities. This integration allows advertisers to pinpoint and address the factors hindering organic traffic conversion, allocate budgets effectively based on historical segment performance, and leverage Analytics segments for audience targeting and creative optimization. Collaborating with your SEO team to understand their desired target segments and potential exclusions can significantly enhance campaign effectiveness. Paid campaigns typically generate rapid results, making them ideal for testing new content or layout variations identified through Analytics insights.
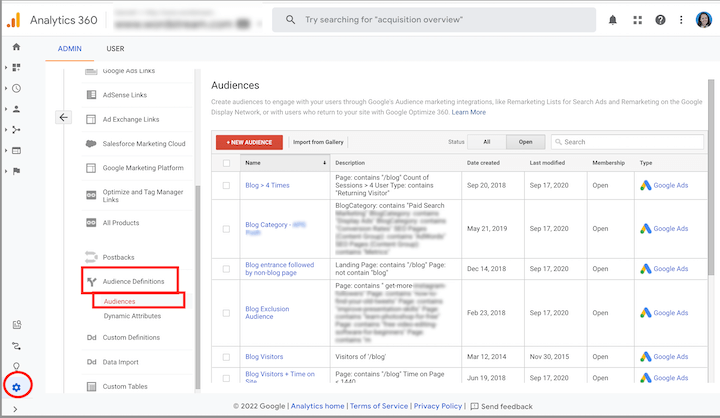 Important: Keep in mind that Analytics segments can sometimes be too small for independent campaigns. Maintain transparency with your team regarding the feasibility of targeting specific segments.
Important: Keep in mind that Analytics segments can sometimes be too small for independent campaigns. Maintain transparency with your team regarding the feasibility of targeting specific segments.
5. Overlooking Ad Copy Nuances
Compelling ad creatives are essential for driving profitable actions. However, generic messaging can diminish their impact. By segmenting audiences and tailoring ad copy to their specific preferences, you can significantly enhance resonance. For instance, understanding whether a particular group responds better to “marketing tools” or “marketing software” can significantly improve message clarity.
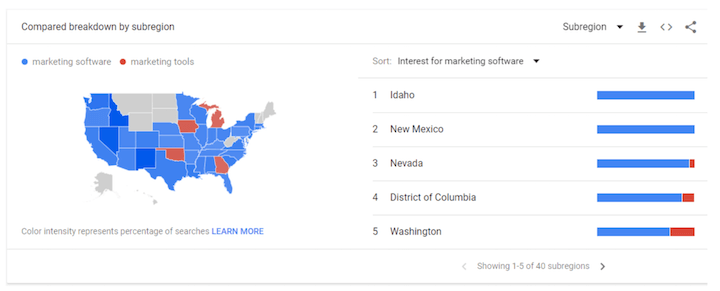 Strive for specificity in your targeting, whether using native audiences or remarketing lists. Targeting “pet owners” without specifying pet types can lead to wasted ad spend.
When crafting ad copy for remarketing lists, acknowledge the existing interaction history with prospects and address potential objections to conversion.
Strive for specificity in your targeting, whether using native audiences or remarketing lists. Targeting “pet owners” without specifying pet types can lead to wasted ad spend.
When crafting ad copy for remarketing lists, acknowledge the existing interaction history with prospects and address potential objections to conversion.
6. Targeting Excessively Small Audiences
Ad algorithms rely on data to function optimally, and targeting overly small audiences can hinder campaign performance. If an audience falls below a certain threshold (typically around 1000 users), it becomes ineligible for ad serving across most platforms. When utilizing a customer list as the foundation for a Lookalike or Similar Audience, be aware that the processing time can take up to 48 hours. Until then, the audience might display a “too small to serve” error. While you should continue building audiences for future targeting, it’s essential to monitor their size and refrain from premature activation.
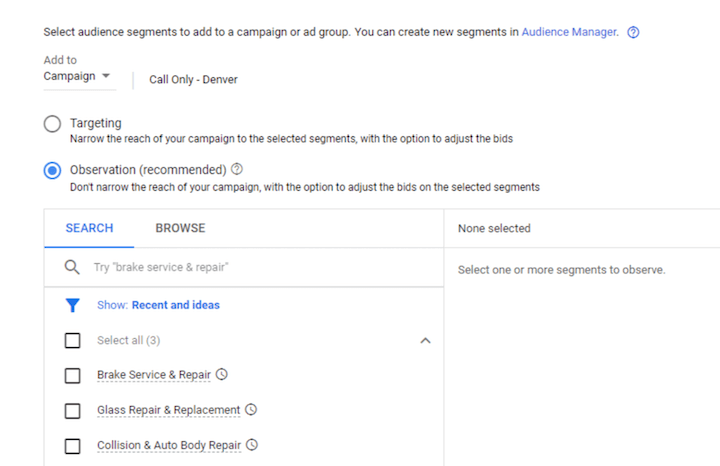
7. Disregarding Observation Mode
Audiences can be applied in either “target and observe” or “observe” mode. This selection determines whether the chosen audience directly influences budget allocation. In “target and observe” mode, the audience needs to be sufficiently large to ensure ad serving. Therefore, starting new audiences in “observe” mode is advisable. Additionally, Smart Bidding algorithms tend to disregard observation audiences and focus solely on fulfilling the defined Smart Bidding objective.
8. Lacking a Clear Brand Positioning Strategy
Strategically utilizing audiences in branded and competitor-targeted campaigns can significantly enhance budget allocation and messaging relevance. Two primary approaches can be adopted for these campaigns:
- Branded campaigns with organic traffic excluded: This strategy protects cheaper organic clicks from cannibalizing general service campaign budgets.
- Branded campaigns targeting brand-aware users: This approach involves creating separate ad groups, one targeting users on remarketing lists and the other excluding them. Both strategies can be effective, and the choice depends on your specific goals and attribution model. If attribution is a concern, the first approach is generally recommended. Conversely, if you trust your tracking and all teams rely on a unified reporting source, the second approach tends to yield better results. When implementing competitor campaigns, consider targeting your existing customer lists to address potential reasons for churn and retain valuable customers.
9. Implementing Siloed Remarketing Strategies
One of the most effective ways to leverage remarketing lists is by applying them across different channels as seeds for Lookalike/Similar Audiences. This cross-channel marketing strategy enables you to reach high-potential customers on platforms where they might not have been captured otherwise. Moreover, this approach allows for budget-efficient testing on new channels while mitigating risks through audience targeting.
10. Failing to Allocate Sufficient Budget for Remarketing
A common mistake advertisers make is merging remarketing budgets with general service campaigns and expecting immediate results. Despite focusing on a more refined audience, remarketing campaigns require dedicated budgets for optimal performance. Ensure you allocate sufficient daily budgets to facilitate campaign ramp-up and goal achievement. As a general guideline, allocate 15-20% of your overall paid campaign budgets to remarketing, especially during the initial stages. Depending on industry auction dynamics, some brands might need to allocate a larger portion of their budget to remarketing efforts.
Enhancing Retargeting Campaign Performance
Remarketing is a potent tool in digital marketing, delivering optimal results when anchored in first-party data and integrated campaign strategies. Here’s a concise summary of the tips provided:
- Prioritize first-party data targeting (customer lists).
- Embrace similar audiences for expanded reach.
- Recognize the power of audience exclusions.
- Integrate Analytics audiences for enhanced SEO collaboration.
- Use terminology that resonates with your audience.
- Ensure audience sizes are sufficient for ad serving.
- Understand the distinction between “target & observe” and “observe” modes.
- Establish a clear brand positioning strategy.
- Leverage remarketing lists across multiple channels.
- Allocate dedicated budgets for remarketing campaigns.