As an online store owner, you understand that Google Merchant Center is key for managing your product info and appearing on Google Shopping. But, with so many options, it’s easy to make mistakes that hurt your sales. This guide will cover ten common Merchant Center errors, helping you avoid them and boost your results.
Content
- Google Merchant Center tips for beginners
- Google Merchant Center mistakes to avoid
- Google Merchant Center optimization: a real-world example
Google Merchant Center: What to know before you start
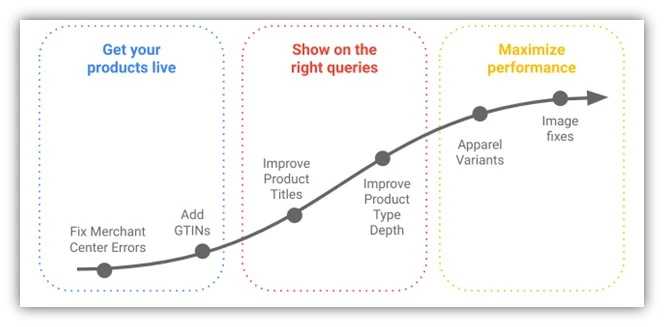
Before diving into Google Merchant Center feed optimization, it’s vital to understand its benefits: better search matching, higher click-through rates (CTR), and increased conversions. The first step is getting your products listed, meaning your product feed meets Google’s rules and all products are approved in your Merchant Center account. To keep them listed, follow Google Shopping guidelines. This prevents product disapproval and account suspension. Next, ensure your products appear for the right searches. Optimize titles, descriptions, and attributes with relevant keywords matching user searches. Finally, maximize product performance with high-quality images and competitive pricing. Regularly review and update product information for accuracy.
 **
****Want to boost your Google Shopping Ads? Get a free account optimization report with our Google Ads Grader!
10 Google Merchant Center mistakes to avoid
Let’s break down Merchant Center health and feed optimization in detail.
1. Using irrelevant or inaccurate product categories
Product categories are crucial for organization and matching user searches. Choosing wrong categories confuses customers and reduces visibility. For instance, a shirt should be categorized under “Apparel & Accessories > Clothing > Shirts & Tops,” not “Home & Garden > Furniture > Chairs.” Avoid custom or duplicate categories to prevent inconsistencies.
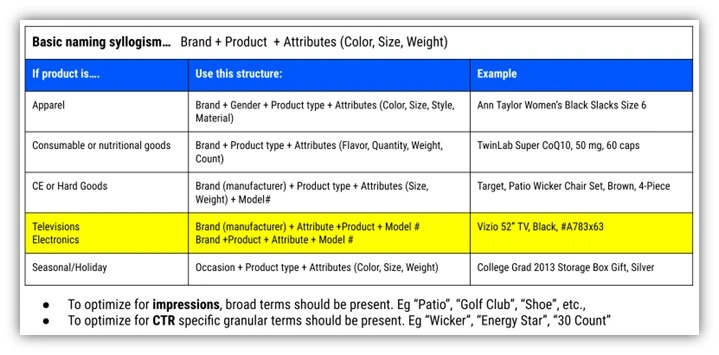
2. De-optimized product titles
Well-crafted titles with relevant keywords and key information significantly improve product visibility and click-through rate. They’re vital for matching searches with products. Include details like brand, gender, product type, and attributes (color, size) aligned with your goals, like attracting new customers or raising brand awareness. This improves impressions, ranking, and performance. Experiment to find what works best for you. Improving the visibility of your brand placement in titles is crucial. For high brand search volume, place it at the beginning. For low volume, consider removing or placing it at the end. Test different options.
3. Forgetting about your descriptions
Detailed product descriptions are crucial for Shopping Ads quality, triggering, ranking, and visibility. Keyword-rich and user-friendly descriptions improve search result visibility. Aim for descriptions between 500-5000 characters. However, most current Google Merchant Center descriptions are under 500 characters.
4. Using low-quality or mismatched images
Product images are your storefront, attracting customer attention. Low-quality or irrelevant images harm credibility, CTR, and conversions. Use high-resolution images accurately representing your products, matching your website’s style and branding. Maintain consistent image sizes and aspect ratios, avoiding watermarks, promotional text, or distractions.


5. Neglecting mobile optimization
With growing use of mobile devices for online shopping, optimize your product data and website for mobile users. Neglecting this means missing out on traffic and conversions. Ensure mobile-friendly product data that displays correctly on small screens. Optimize your website for mobile speed and usability: use responsive design, optimize images, and reduce loading times.
**6. Overusing promotional text and special characters
** Highlighting product features and benefits is important, but excessive promotional text and special characters are counterproductive. Google might see them as spam, and customers might find them annoying or confusing. Use them strategically and sparingly, like in titles or descriptions. Follow Google’s guidelines, avoiding all caps, excessive exclamation points, emojis, or symbols.
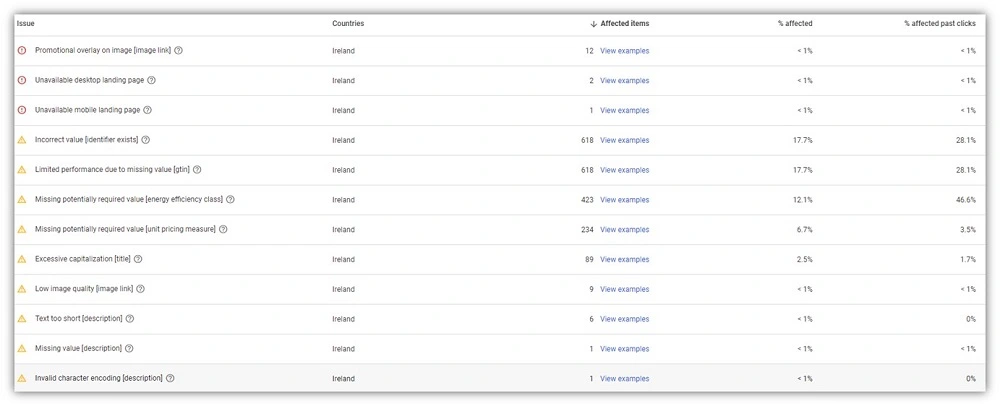
**7. Ignoring feed errors and warnings
** Ignoring feed errors and warnings is a common mistake. Merchant Center uses feeds for product data, and any issues can hinder product visibility, cause inaccuracies, or lead to disapproval. Not addressing these regularly harms performance and customer experience. Regularly check your feed for issues. Use Merchant Center’s diagnostic and feed rules to identify and fix problems. Ensure your feed adheres to Google’s requirements, including data quality, product identifiers, and country-specific rules. Regularly monitor your feed health and set up alerts for critical issues. This ensures product visibility, accuracy, compliance, and avoids delays or penalties.
**8. Not using custom labels
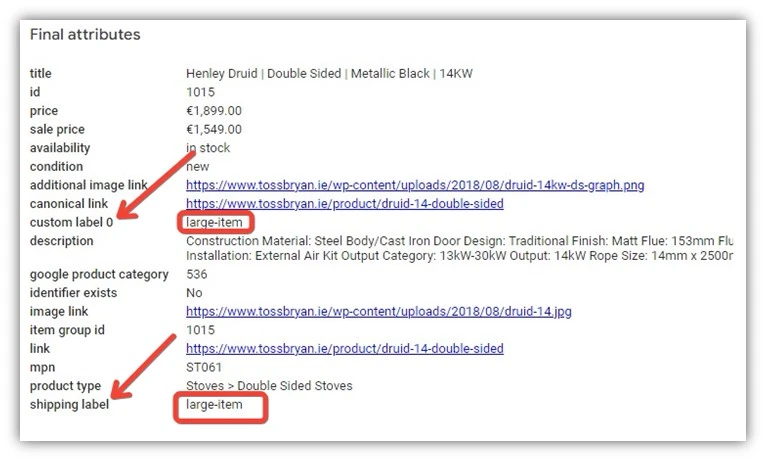
** Custom labels in Google Merchant Center are powerful for grouping products based on margin, seasonality, popularity, or product type. This helps optimize bidding, reporting, segmentation, and tailor promotions and ad copy for specific audiences. Identify relevant custom labels and use them consistently. In the example, the merchant uses custom labels to differentiate item sizes for ad group segmentation. They also use ‘shipping-label’ to indicate varying shipping costs per size group.
**9. Using vague or generic product identifiers
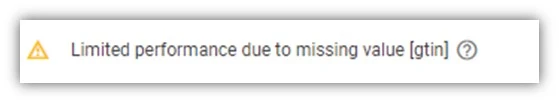
** Firstly, understand GTINs (Global Trade Item Numbers): unique 14-digit codes (or EAN/ISBN) assigned to products, mandatory for all products with them. Inaccurate GTINs cause feed issues but are easily fixed. Correct GTINs streamline feed management. Product identifiers (GTINs, MPNs, brand names) are crucial for matching products with user searches, ensuring accuracy and relevance. Vague identifiers create confusion, especially for product variations or bundles. Use unique and accurate identifiers following Google’s guidelines, matching your website product pages. Include all necessary identifiers and variants, fixing mismatches or missing data.
**10. Forgetting about sale price annotations
** Using a “SALE PRICE” attribute in your feed attracts customers and increase sales. However, meet these requirements:
- The base price must have been charged for at least 30 consecutive days in the past 180 days. This ensures the sale price is genuine and customers get a real deal.
- The base price must be valid. The original price must be accurate, reflecting its actual past selling price. A false base price is misleading and erodes customer trust.
- The sale price must be lower than the base price. The sale price should be lower, with a significant discount to attract customers.
- The discount of the sale must be greater than 5% and less than 90%. This ensures the sale is not a minor adjustment or an attempt to clear unwanted stock. Excessively high discounts raise doubts about product quality or the sale’s legitimacy. Meeting these requirements differentiates your ads, creates urgency, and excites customers, leading to more clicks, conversions, and sales.
 **
****Plan your business growth with Google Shopping Ads and more using our free growth strategy template!
Real-world Google Merchant Center optimization example
Let’s apply our knowledge with a real-world example. An online retailer selling outdoor gear (tents, backpacks, hammocks) wasn’t seeing results with Google Shopping. Their product titles and descriptions were too general, lacking specific keywords and details users searched for. For example, a four-person tent was simply titled “Camping Tent.” To improve, they revamped their product information, aligning it with user searches. They added brand names and GTINs for visibility and credibility. This led to significant improvements in CTR and conversion rate (CVR). They achieved a 200% CTR increase and a 50% CVR increase within a month. The new titles and descriptions were more informative, descriptive, and relevant, using keywords matching user intent. For instance, the four-person tent became “Coleman Family Camping Tent for 4 People – Waterproof, Easy Setup, and Durable,” highlighting key features and benefits.
 Adding brand names and GTINs boosted sales, as users trust products with verifiable information. A study by Google showed products with GTINs have a 20% higher conversion rate.
The takeaway: optimizing product titles, descriptions, and data significantly impacts Google Shopping performance and ROAS. Align your product data with user intent, add brand names and GTINs, use relevant high-quality images and videos to attract customers, and stand out from competitors.
Adding brand names and GTINs boosted sales, as users trust products with verifiable information. A study by Google showed products with GTINs have a 20% higher conversion rate.
The takeaway: optimizing product titles, descriptions, and data significantly impacts Google Shopping performance and ROAS. Align your product data with user intent, add brand names and GTINs, use relevant high-quality images and videos to attract customers, and stand out from competitors.
Start improving your Google Merchant Center feed today
Optimizing your Google Merchant Center feed benefits your business by improving search relevance, increasing CTR, and driving conversions. To achieve this, follow Google Shopping guidelines, ensure your products are listed and remain visible, optimize titles and descriptions, and maximize performance with high-quality images and competitive pricing. Regularly review and update your product information for accuracy, a positive user experience, and business growth. You’re not alone in managing your Google Merchant Center. Discover how our solutions can help optimize your product feed and maximize shopping campaign success for your business! Here’s a recap of ten Google Merchant Center mistakes to avoid for an optimized feed:
- Using irrelevant or inaccurate product categories
- De-optimized product titles
- Forgetting about your descriptions
- Using low-quality or mismatched images
- Neglecting mobile optimization
- Overusing promotional text and special characters
- Ignoring feed errors and warnings
- Not using custom labels
- Using vague or generic product identifiers
- Forgetting about sale price annotations